Question Bank – Pediatric Ocular
Quiz Summary
0 of 32 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 32 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 32
1. Question
How far behind the globe of the eye is the optic nerve sheath measured?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 32
2. Question
Which of the following statements regarding ocular ultrasound literature is FALSE?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 32
3. Question
Measuring the optic nerve sheath at an angle (rather than parallel to) the ultrasound beams will most likely:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 32
4. Question
Which of the following is an advantage of optic nerve sheath diameter over optic disc elevation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 32
5. Question
What is the purpose of setting the ultrasound transducer to the lowest mechanical and thermal index on the ultrasound “ocular setting”?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 32
6. Question
Which of the following is NOT a pearl for optimizing ultrasound of the optic nerve and optic disc?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 32
7. Question
Which of the following optic disc findings is more often a finding in pseudopapilledema rather than true optic disc elevation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 32
8. Question
Which of the following findings are NOT associated with increased probability of elevated intracranial pressure?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 32
9. Question
You attempt to assess the optic disc and optic nerve sheath with ocular ultrasound of a toddler who cries when held still and doesn’t follow instructions to look forwards reliably. Which of the following techniques can you use to obtain the measurements you need?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 32
10. Question
An asymptomatic 10 year old boy with no history of medical problems agrees to allow you to ultrasound his eyes during ultrasound teaching session. Ocular POCUS shows elevation of the optic disc that is sharp/pointy in appearance and fleeting when the probe is rotated or fanned. The optic nerve sheath is 6.0mm in diameter. Neurological exam is normal. Which of the following is the next best step in management for this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 32
11. Question
A 5 year old boy presents for daily emesis in the morning for the past 2 weeks. He has endorsed new onset headache to his parents in the mornings. Neurologic exam is limited by cooperation, as he does not seem to understand the instructions which his mom says is unusual for him. There is no family history of migraines. Fundoscopic exam is unsuccessful. Ocular ultrasound shows a flat optic disc and optic nerve sheath diameter is 5.7mm.
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 32
12. Question
A patient with a VP shunt and history of frequent admissions for VP shunt malfunction presents to the emergency department for vomiting, diarrhea, and one day of subjective fever. His mother endorses that she had similar symptoms the week prior. Temperature and vitals signs in the emergency department are normal. His mother notes that he is tired and seems sad, but otherwise his exam is at baseline. Fundoscopic exam is unsuccessful, ocular ultrasound shows optic disc elevation that measures 0.4mm and optic nerve sheath that is 5.9mm in diameter. Because he has presented frequently for concern for elevated ICP before you consult his chart and you see that the optic nerve sheath is typically 4.3mm when measured between episodes of ICP elevation. Which of the following is the next best step in management?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 32
13. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 32
14. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 32
15. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 32
16. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 32
17. Question
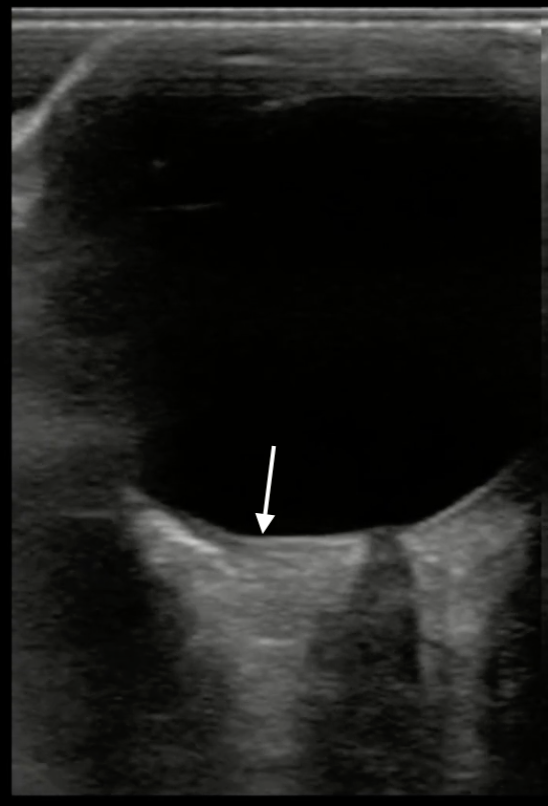
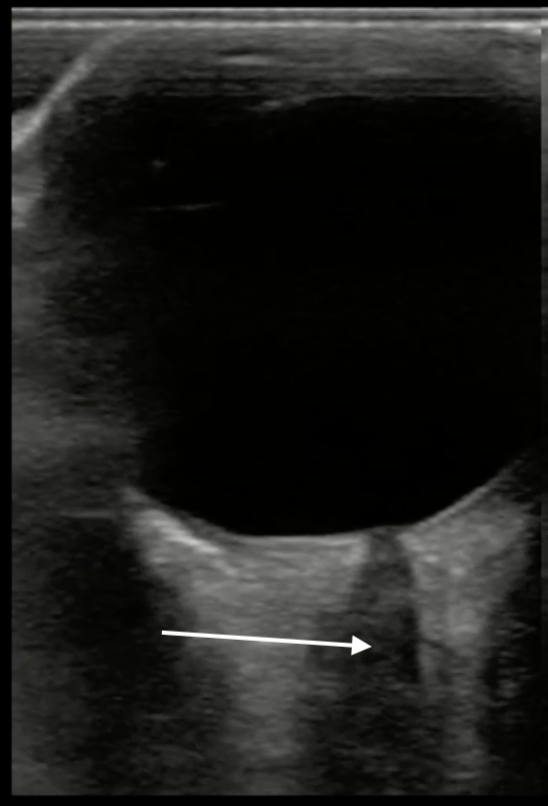
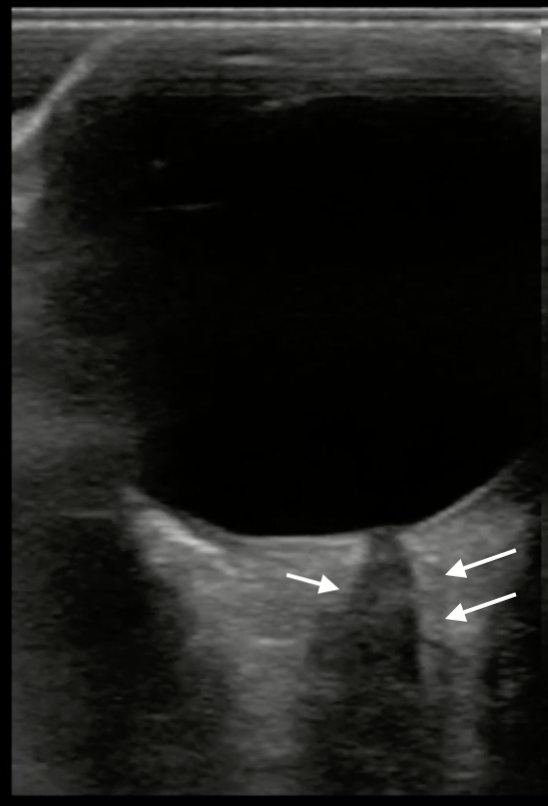
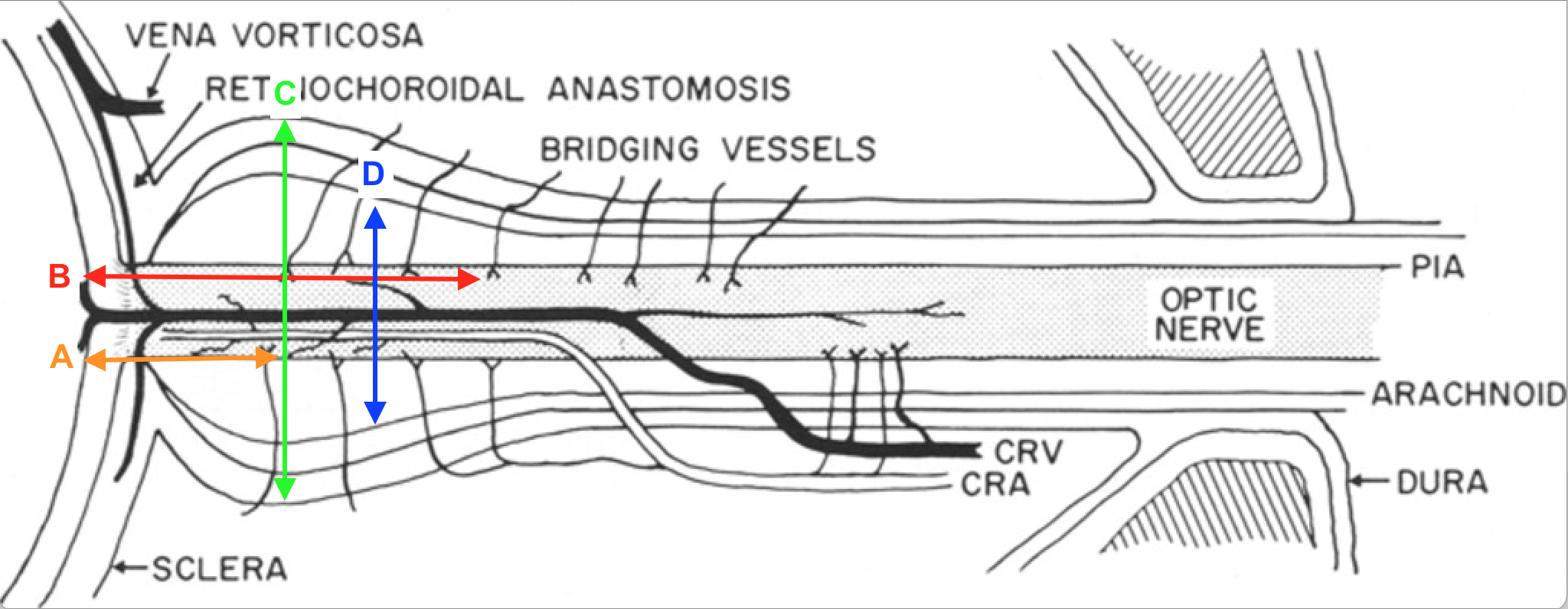
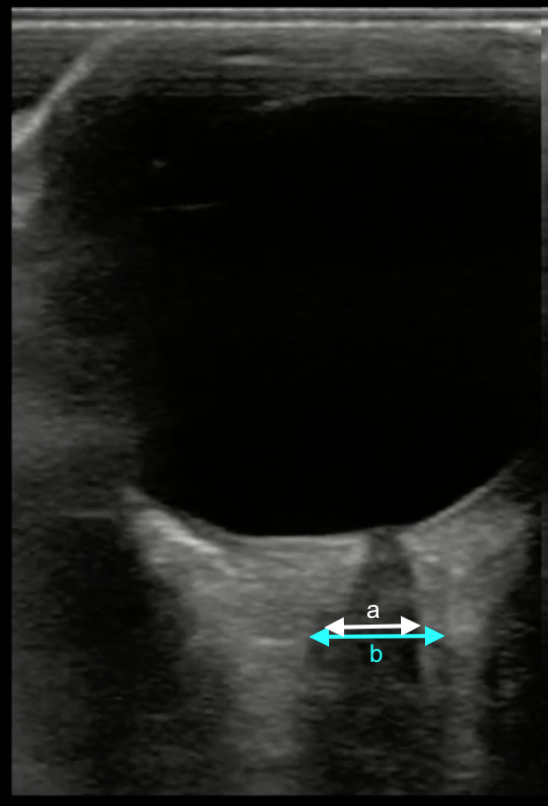
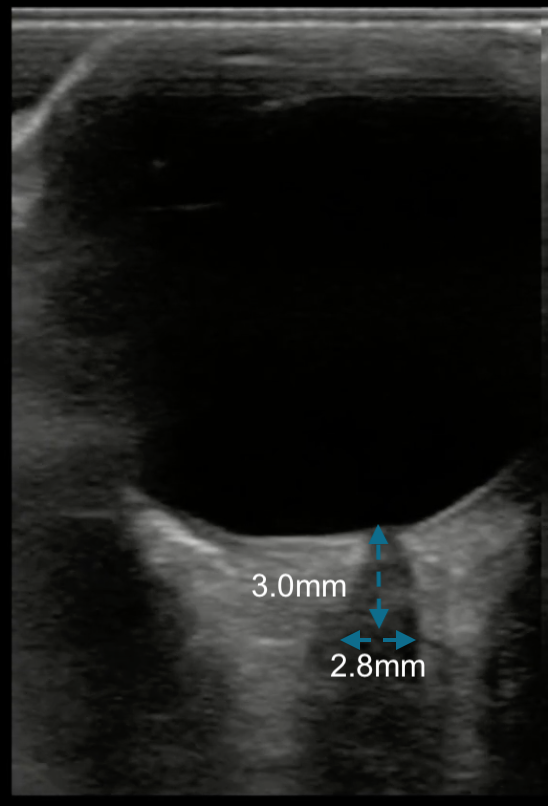
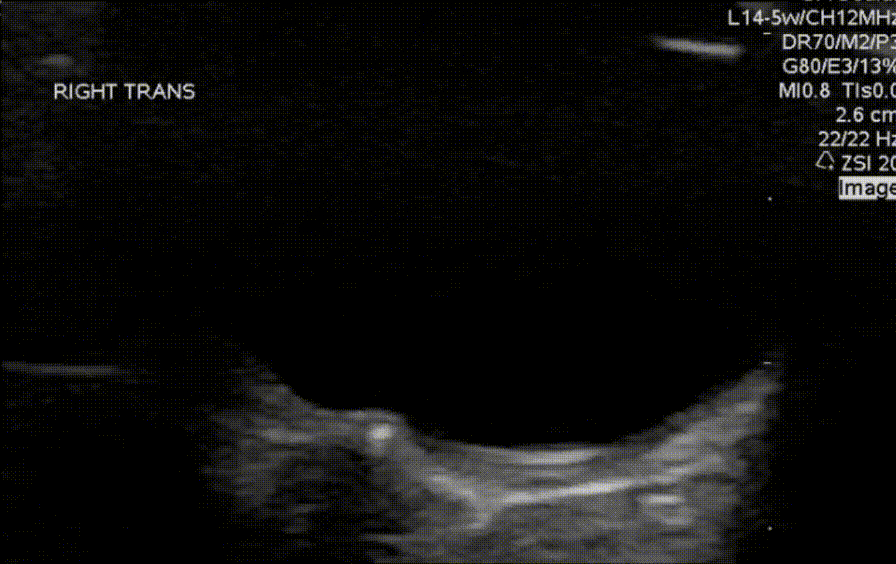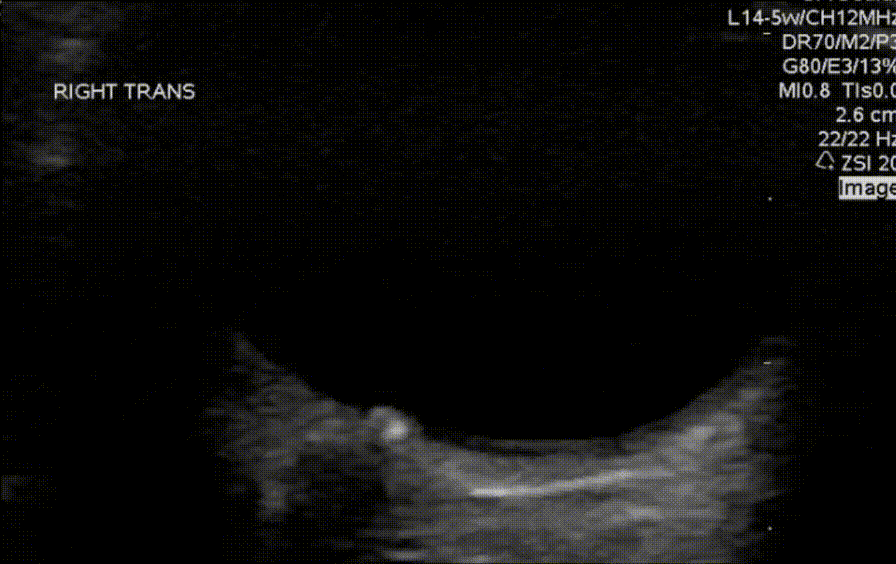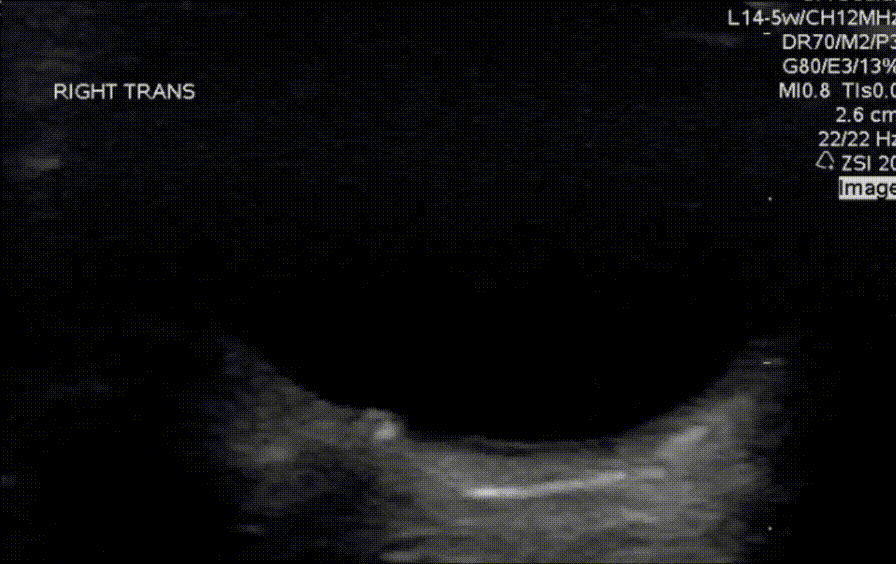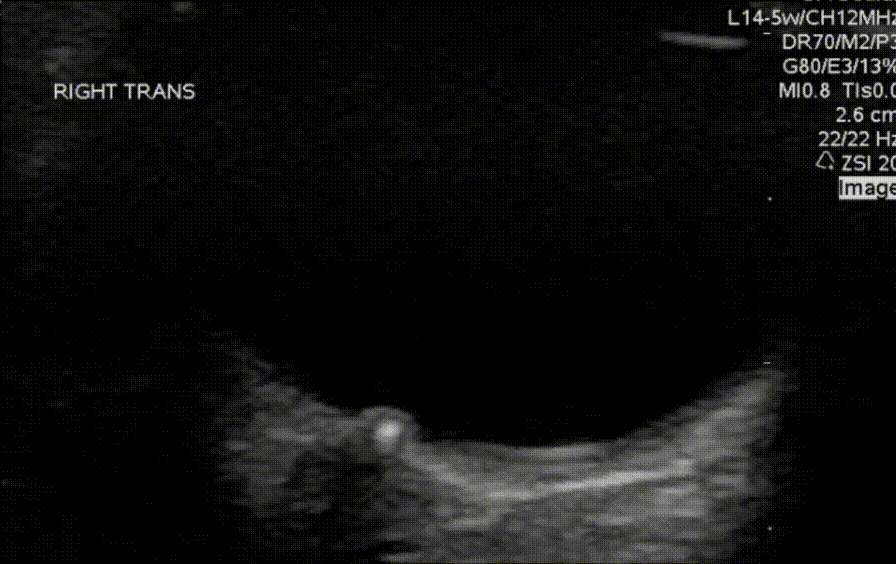
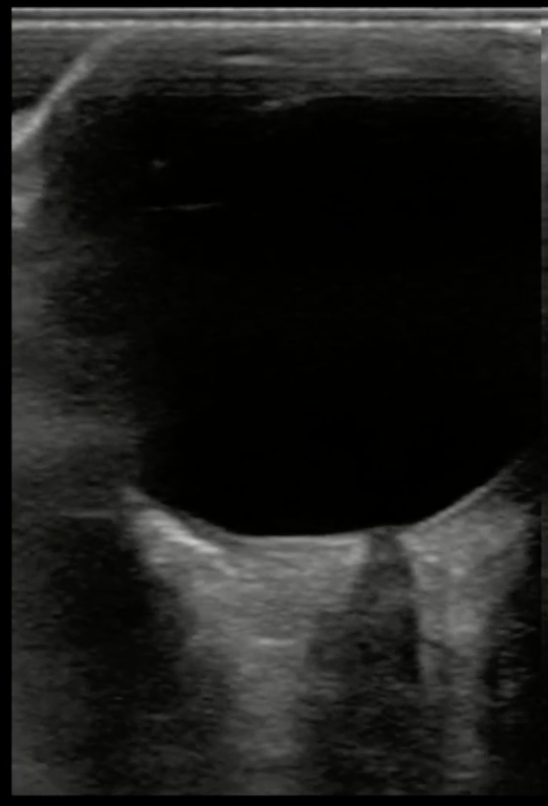
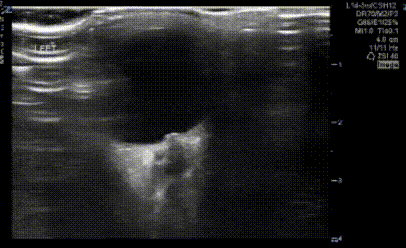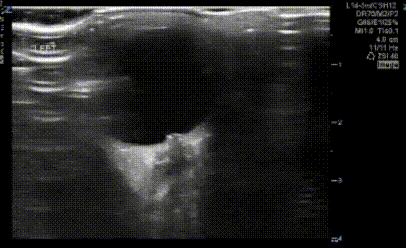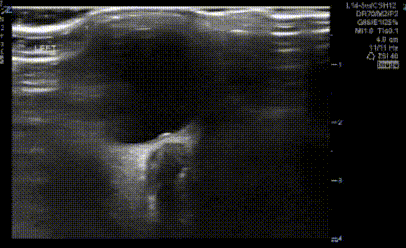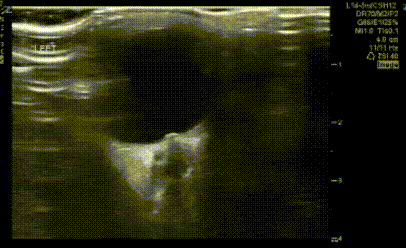
Which of the measurements depicted in the image is the correct way to measure the optic nerve sheath diameter?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 32
18. Question
Which of the following statements is true?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 32
19. Question
When performing ocular ultrasound on a child in your pediatric outpatient clinic presenting for headaches, you note that the optic disc looks a little bulgy. Which if the following is MOST suggestive of true papilledema (as opposed to pseudopapilledema)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 32
20. Question
Which of the following ocular ultrasound findings is more sensitive for elevated intracranial pressure?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 32
21. Question
Which of the following ocular ultrasound findings is more specific for elevated intracranial pressure?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 32
22. Question
Which of the following is a cause for false overestimation of the optic nerve sheath diameter?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 32
23. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 32
24. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 32
25. Question
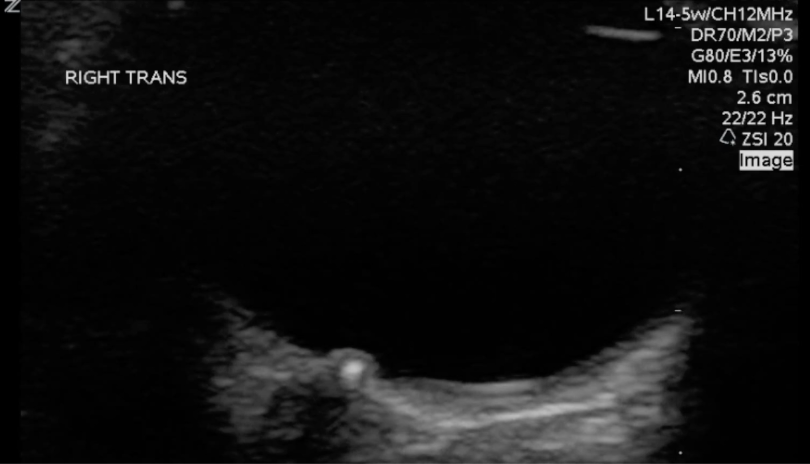
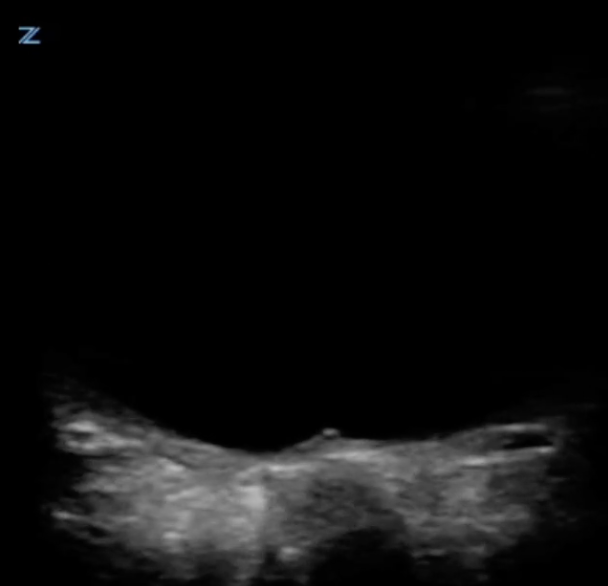
An obese teenage girl taking isotretinoin presents with daily headaches for 2 weeks that have been progressively worsening and are now severe. She states that the headaches feel like they originate behind her eyes and she complains of a rushing or whooshing sound when trying to fall asleep at night.
What findings are shown in the image?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 32
26. Question
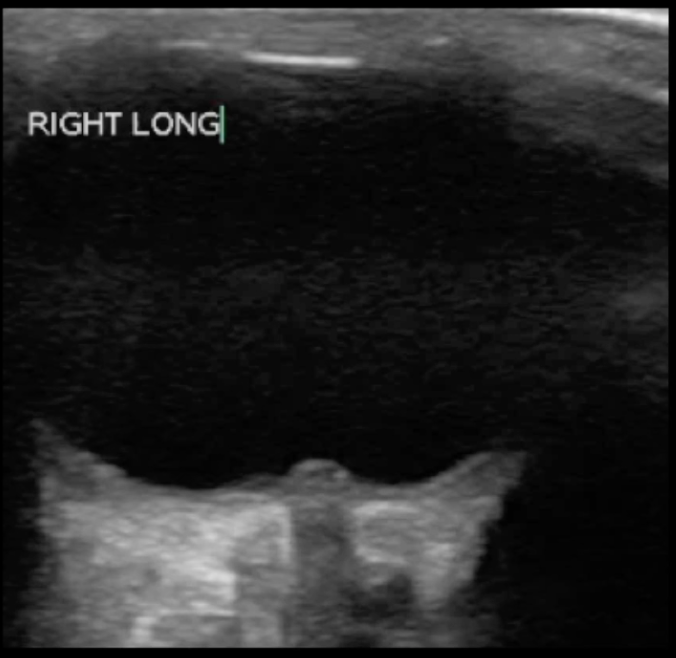
An obese teenage girl taking isotretinoin presents with daily headaches for 2 weeks that have been progressively worsening and are now severe. She states that the headaches feel like they originate behind her eyes and she complains of a rushing or whooshing sound when trying to fall asleep at night. Ocular ultrasound shows the findings below:
What finding is shown in the image?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 32
27. Question
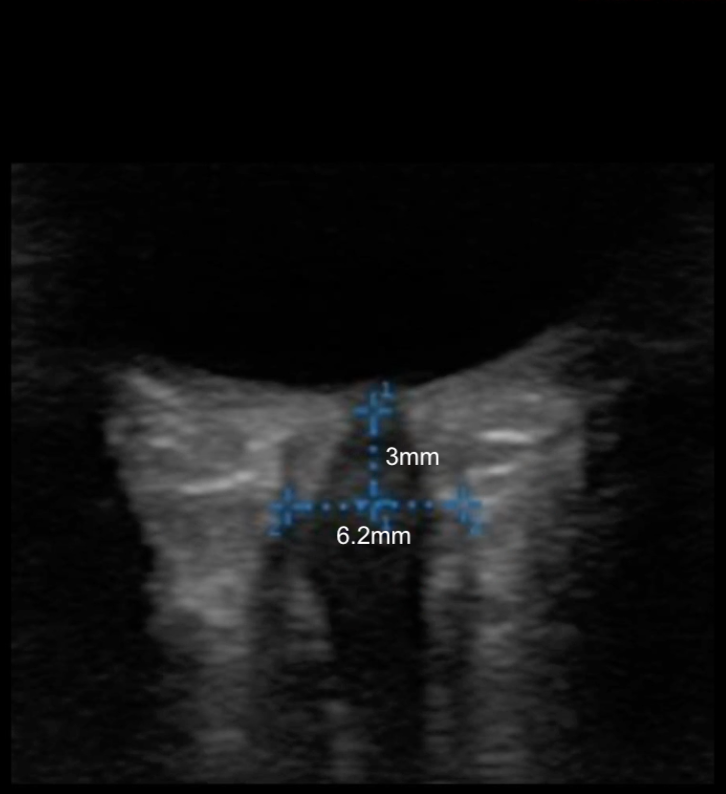
An obese teenage girl taking isotretinoin presents with daily headaches for 2 weeks that have been progressively worsening and are now severe. She states that the headaches feel like they originate behind her eyes and she complains of a rushing or whooshing sound when trying to fall asleep at night. Ocular ultrasound shows the findings below:
What findings are shown in the image?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 32
28. Question
An obese teenage girl taking isotretinoin presents with daily headaches for 2 weeks that have been progressively worsening and are now severe. She states that the headaches feel like they originate behind her eyes and she complains of a rushing or whooshing sound when trying to fall asleep at night. Ocular ultrasound shows the findings below:
What findings are shown in the image?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 32
29. Question
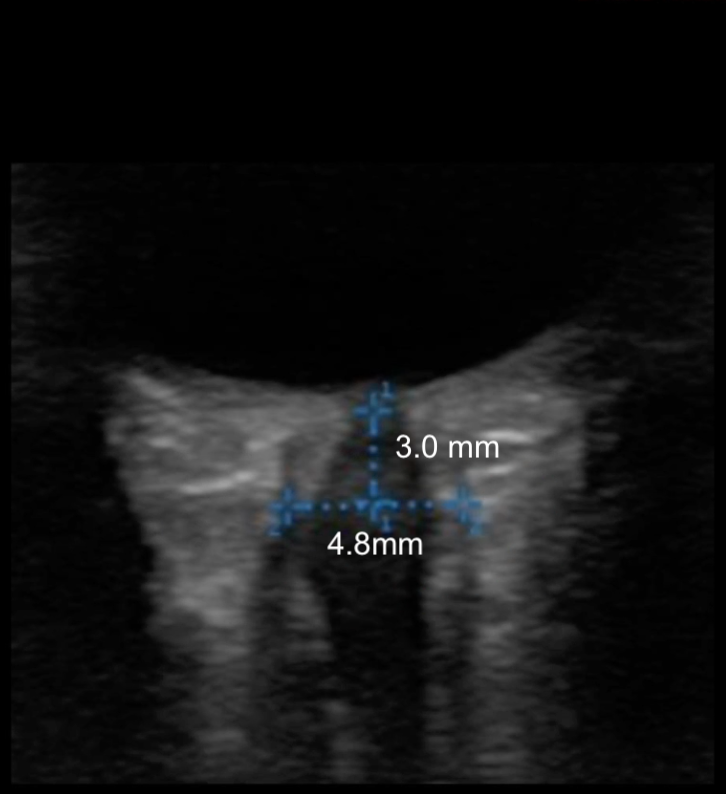
An 8 year old with no past medical history presents for evaluation of headaches. Headaches are frontal and usually occur at the end of the school day, occur about 4-6 times per week, and are less frequent on weekends or holidays. Review of systems and neurological exam is otherwise normal. Ocular POCUS shows the following finding.
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 32
30. Question
A 4yo boy presents with new-onset focal seizures. History is significant for daily headaches and daily emesis for the past 2 weeks.
Which of the following is the most likely etiology of his presentation and findings?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 32
31. Question
A 3 year old child with a VP shunt presents for acute onset of vomiting. He has multiple sick contacts in his family with similar symptoms. On exam, he appears tired and his neuro exam is non focal. Review of his chart shows that in the past his only symptoms of VP shunt malfunction were vomiting and fatigue. Ocular POCUS shows the following:
What is the most likely cause of his vomiting?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 32
32. Question
A 3 year old child with a VP shunt presents for acute onset of vomiting. He has multiple sick contacts in his family with similar symptoms. On exam, he appears tired and his neuro exam is non focal. Review of his chart shows that he has presented with similar symptoms for VP shunt malfunction in the past. Ocular POCUS shows the following:
CorrectIncorrect
Contact form website
Contact form website
"*" indicates required fields
CONTACT US
Get in touch with our team to know more about GUSI.
PRE-REGISTRATION | POCUS FOR PRIMARY CARE IN PERSON COURSE OCT. 2025
Tentative Dates: October 17-18, 2025 | San Francisco, CA
PRE-REGISTRATION | POCUS FOR PRIMARY CARE IN PERSON COURSE APRIL 2025
Tentative Dates: April 2025 | San Francisco, CA
PRE-REGISTRATION | GUSI-OHSU Musculoskeletal Ultrasound for Primary Care & Joint Injection Cadaver Course
Tentative Dates: June 7-8, 2025, Portland, OR
PRE-REGISTRATION | OB POCUS ESSENTIALS COURSE JAN 30 - FEB 2
Jan 30th to Feb 2nd 2025
[elementor-template id=”3620″]