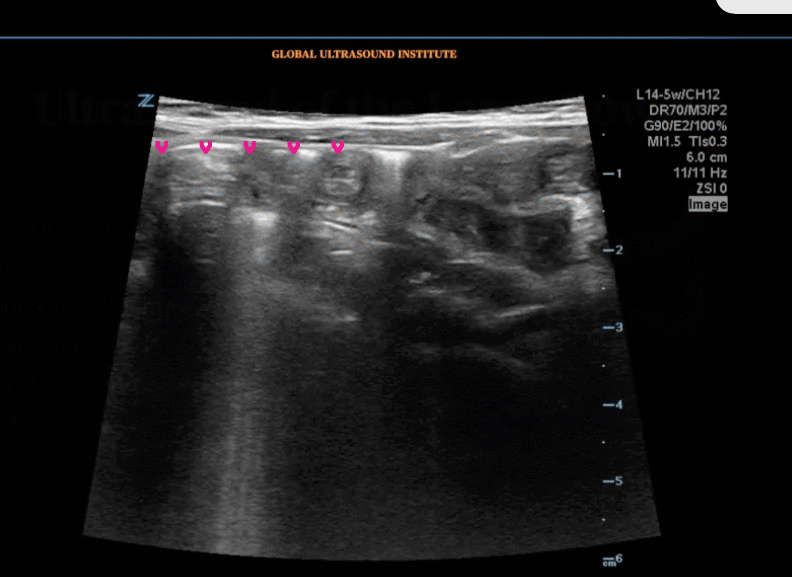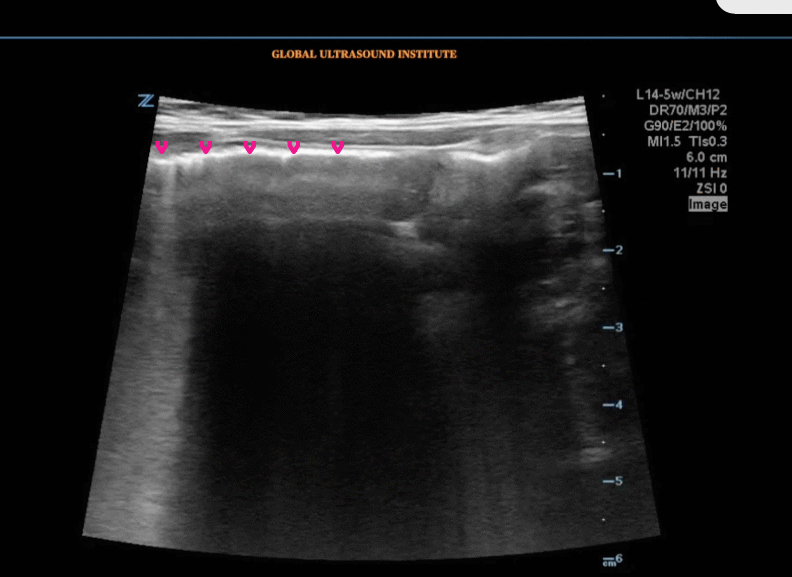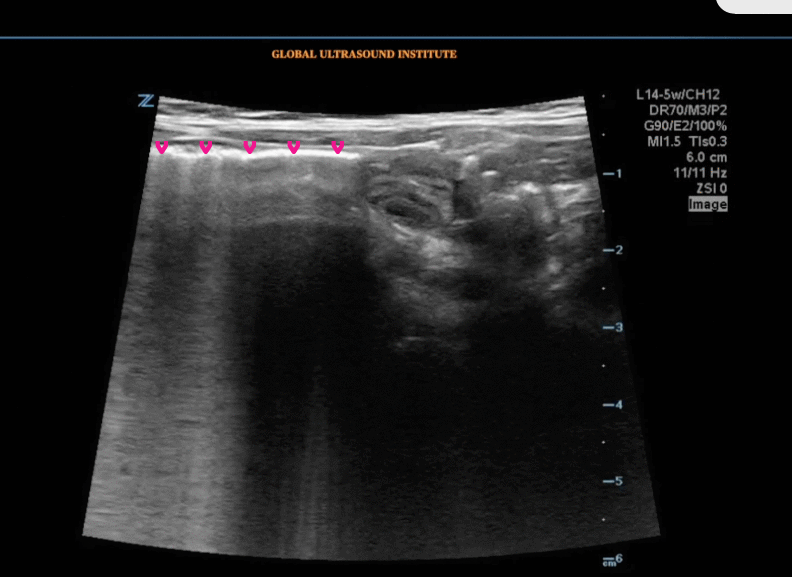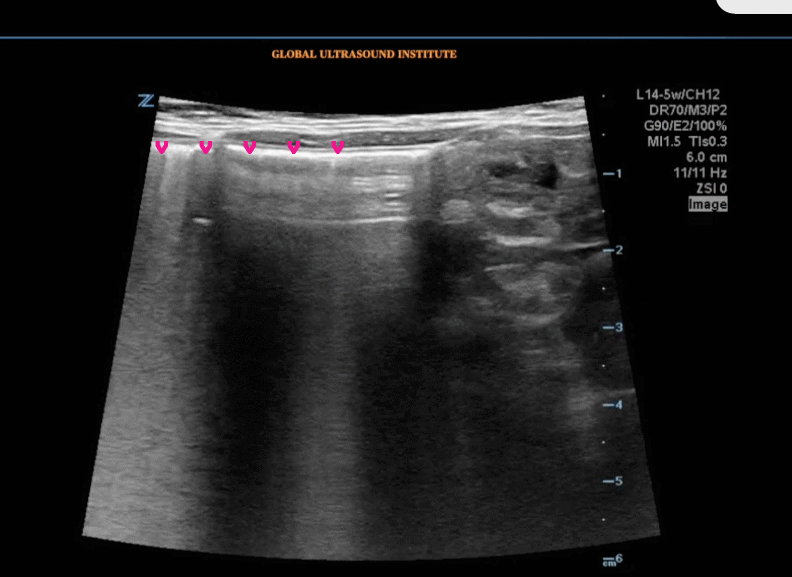
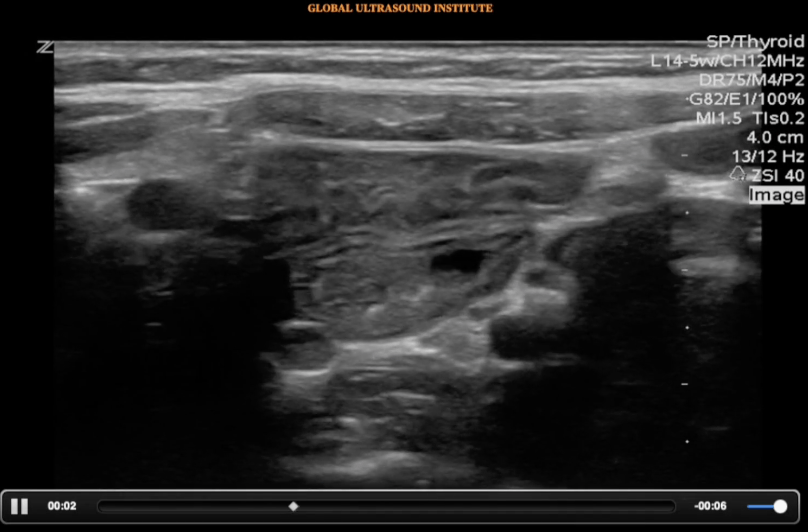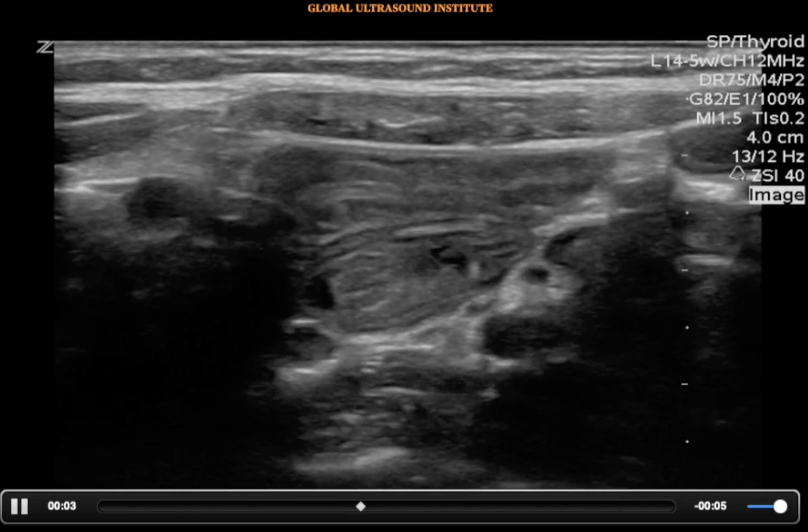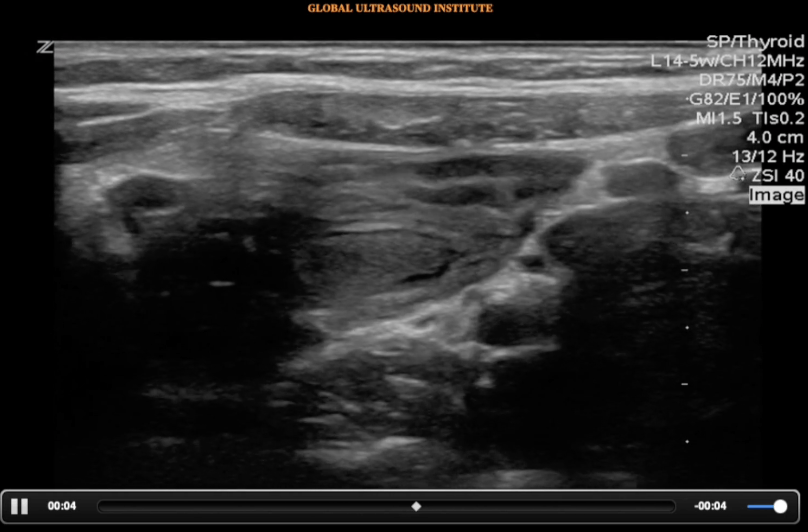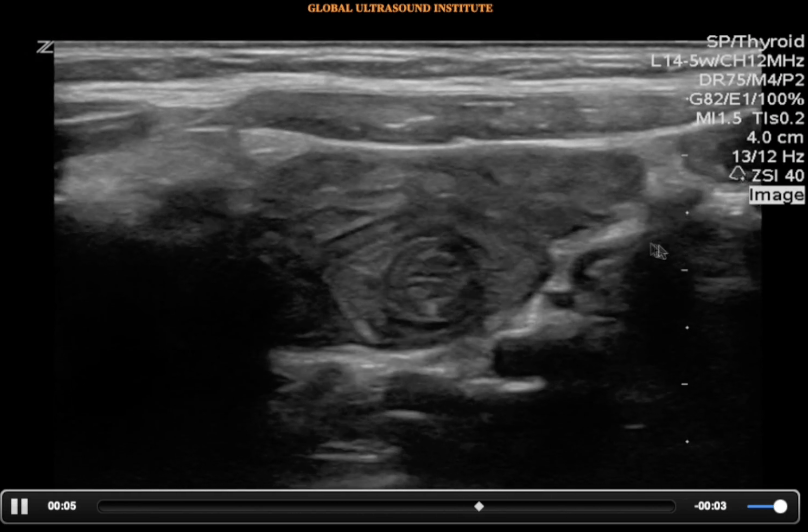
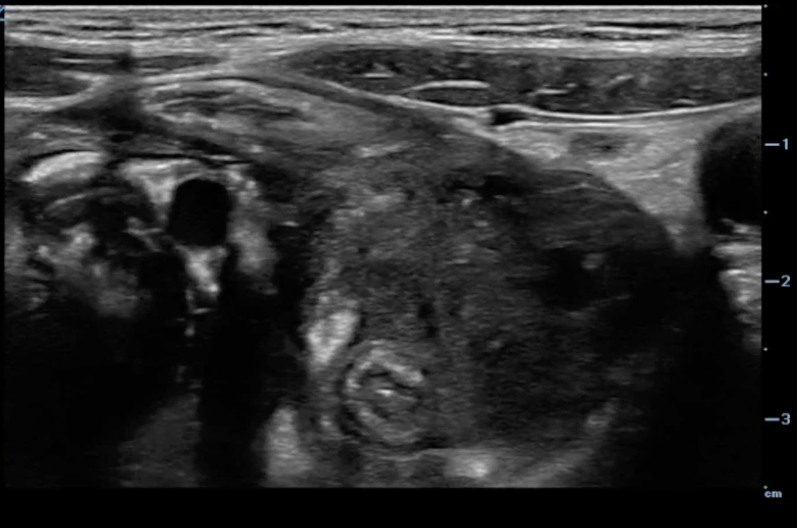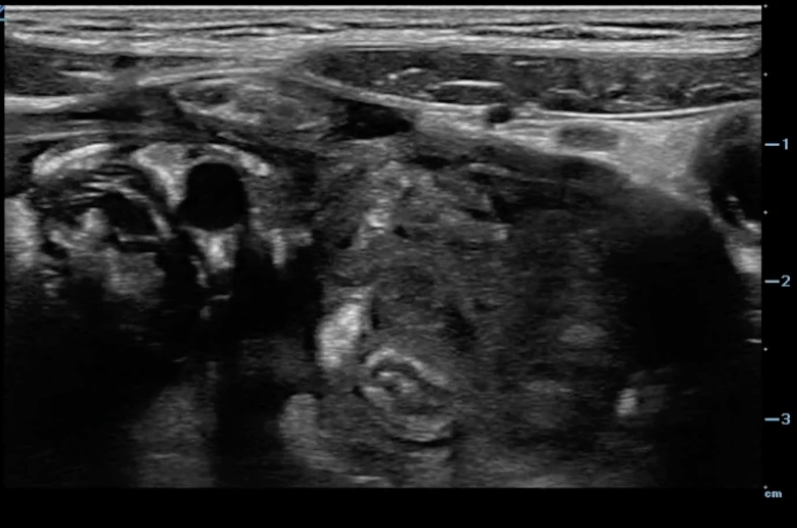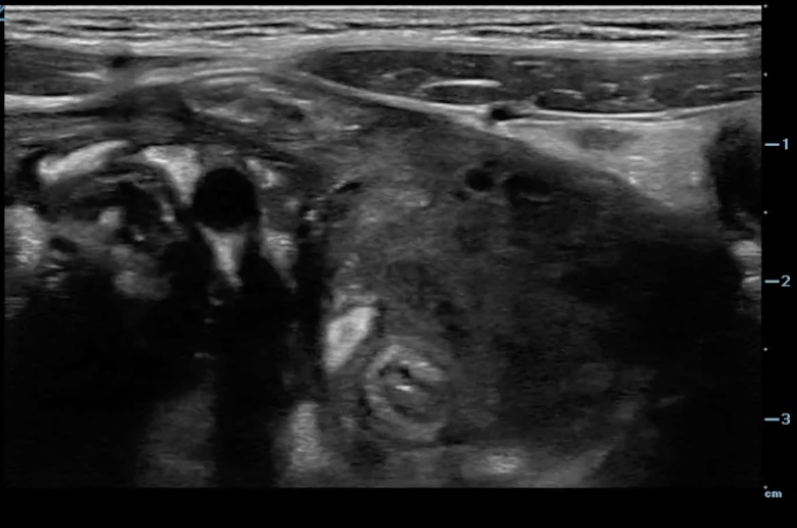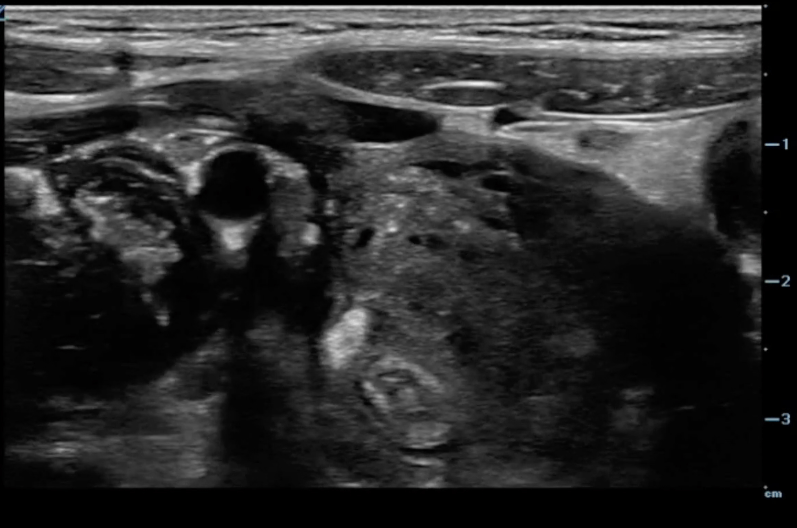
Question Bank – Pedi Abdomen
Quiz Summary
0 of 27 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 27 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 27
1. Question
Per the study by Blumfield et al, “Ultrasound for Differentiation Between Perforated and Nonperforated Appendicitis in Pediatric Patients” (2013), which of the following ultrasound findings had the highest SENSITIVITY for perforated appendicitis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 27
2. Question
The pediatric literature has shown the point of care ultrasound for appendicitis by ED providers is associated with which of the following patient centered outcomes:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 27
3. Question
Per the study performed by Nah et al, “Clinical relevance of the non-visualized appendix on ultrasonography of the abdomen in children” (2017), on review of 160 patients with suspected appendicitis who had a nonvisualized appendix on ultrasound and NO evidence of secondary inflammatory changes, the likelihood of appendicitis is:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 27
4. Question
In their study “Diagnostic Accuracy of History, Physical Examination, Laboratory Tests, and Point-of-care Ultrasound for Pediatric Acute Appendicitis in the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis” (2017) Benabbas et al reviewed 21 studies of POCUS performed in the emergency department by emergency physicians in the diagnosis of appendicitis in pediatric patients. Which of the following findings, when present, was associated with the highest likelihood ratio of true acute appendicitis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 27
5. Question
In the hands of novice providers, ED-performed point of care ultrasound is
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 27
6. Question
When performing POCUS to evaluate a child with suspected appendicitis, you are unable to locate the appendix. Which of the following statements is correct?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 27
7. Question
Which of the following characteristics is typical of large bowel?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 27
8. Question
In distinguishing it from the small bowel, which of the following characteristics is most convincing that you are looking at the appendix?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 27
9. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 27
10. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 27
11. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 27
12. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 27
13. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 27
14. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 27
15. Question
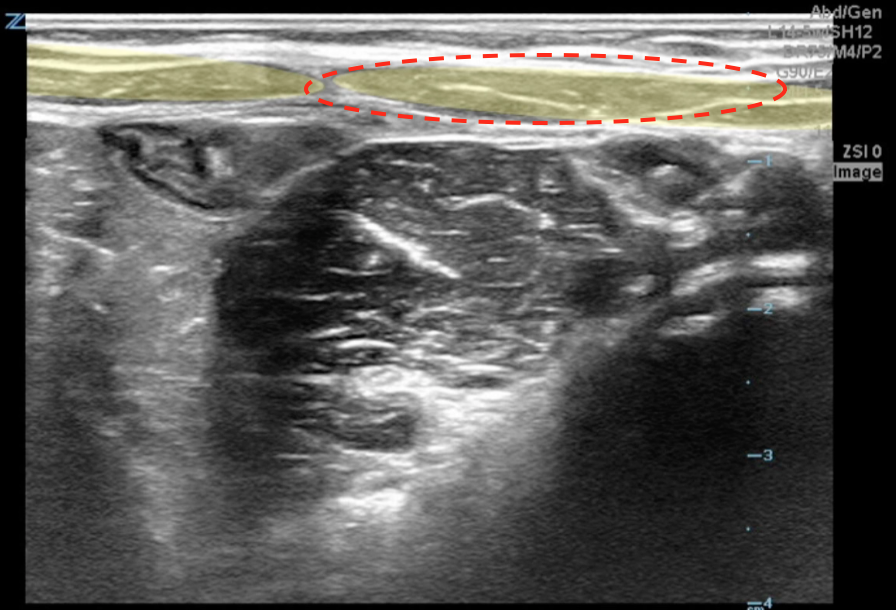
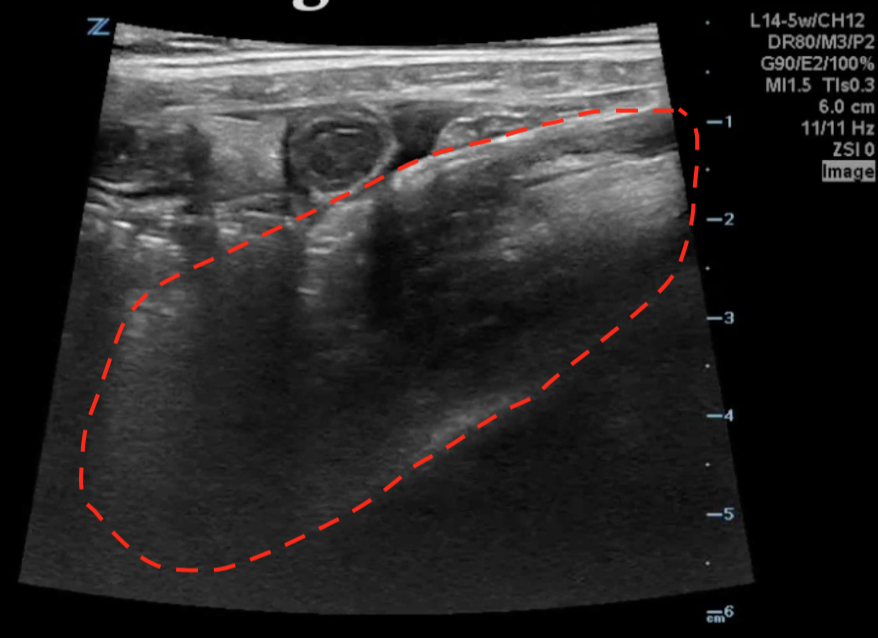
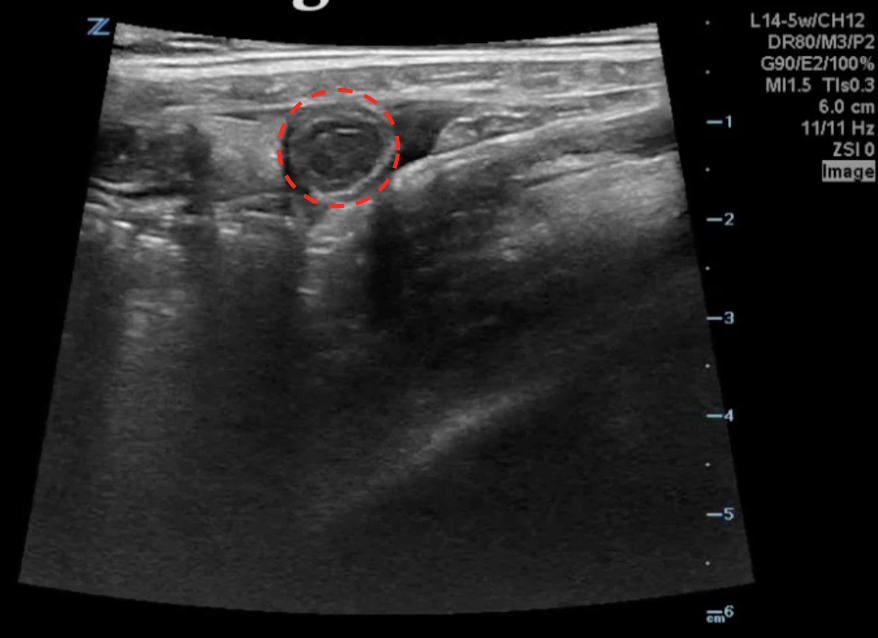
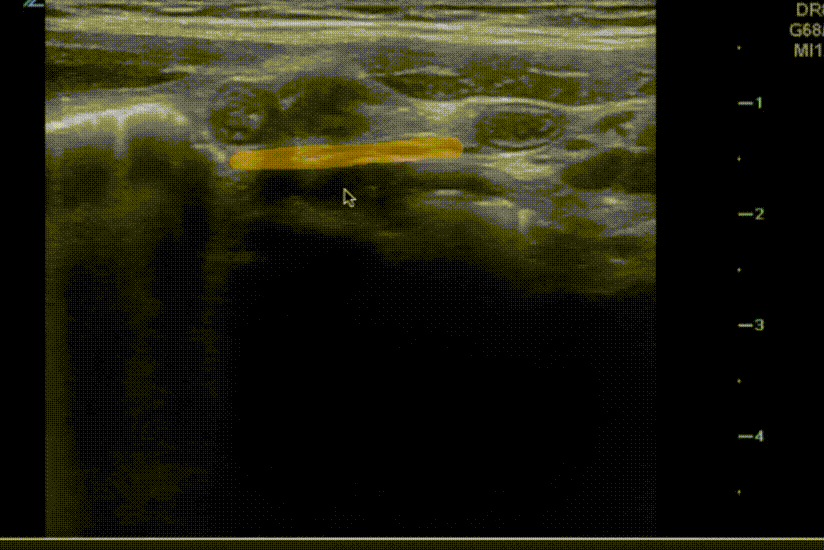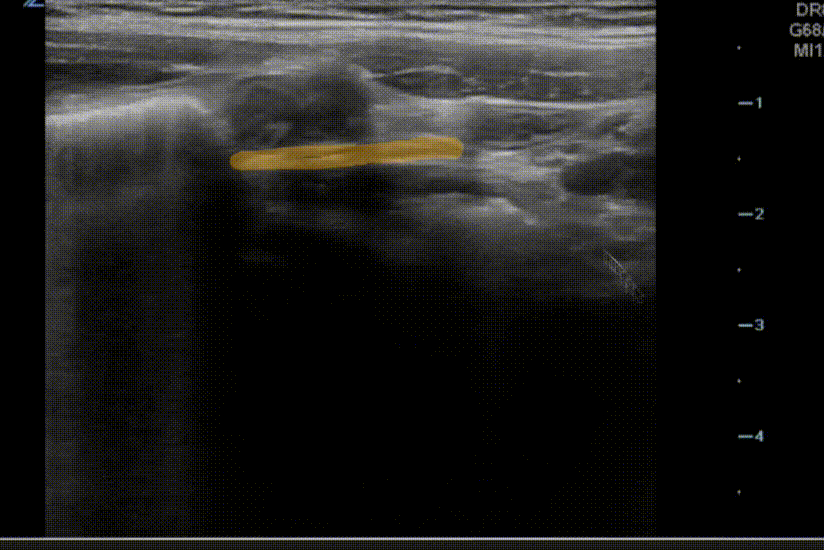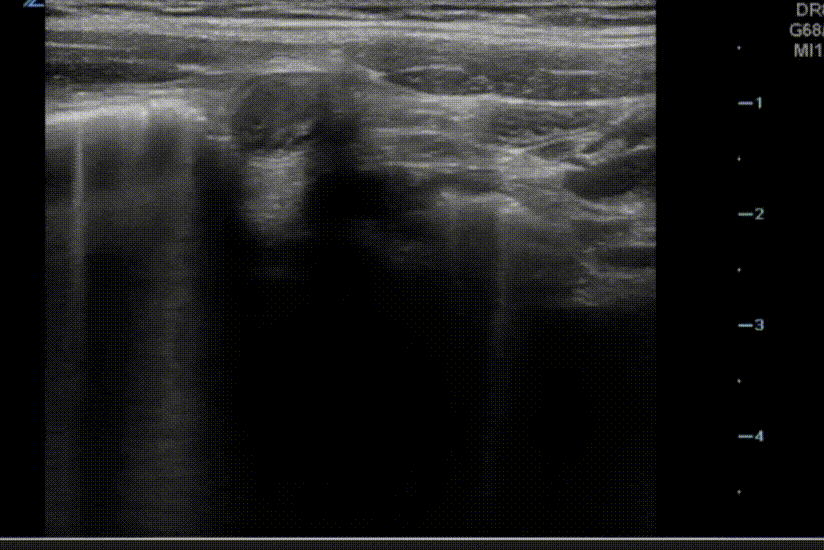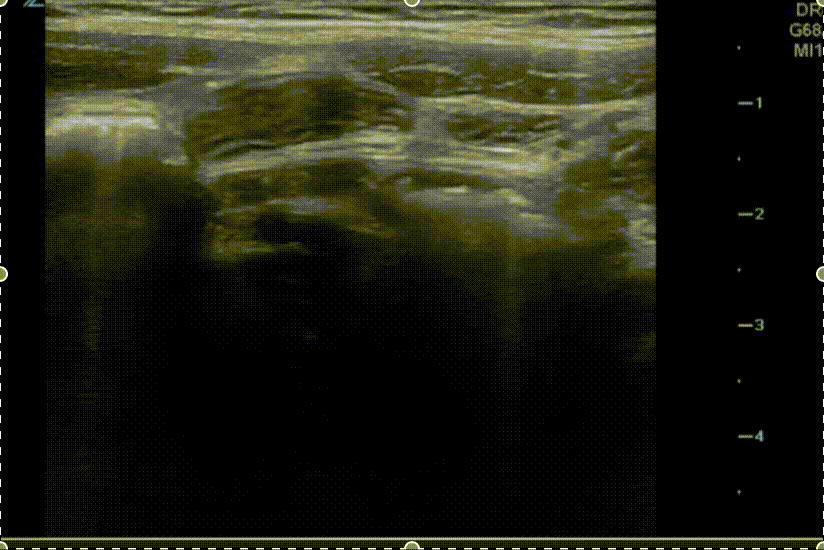
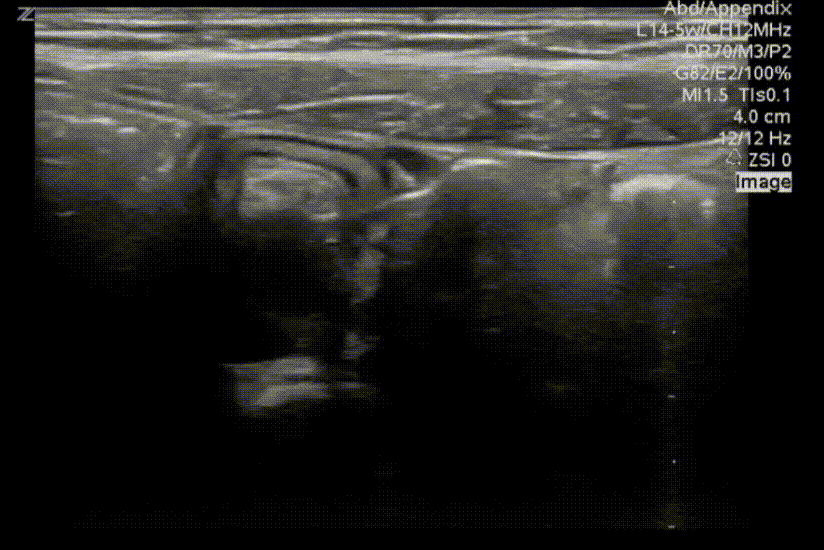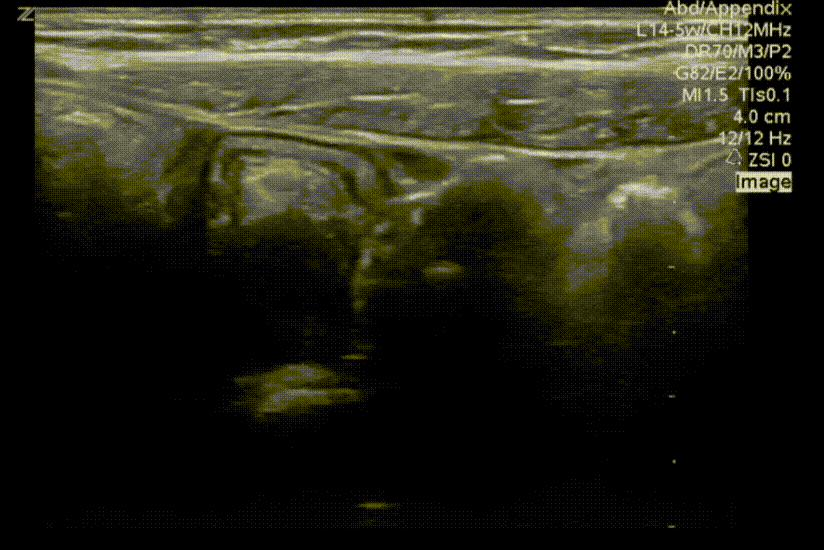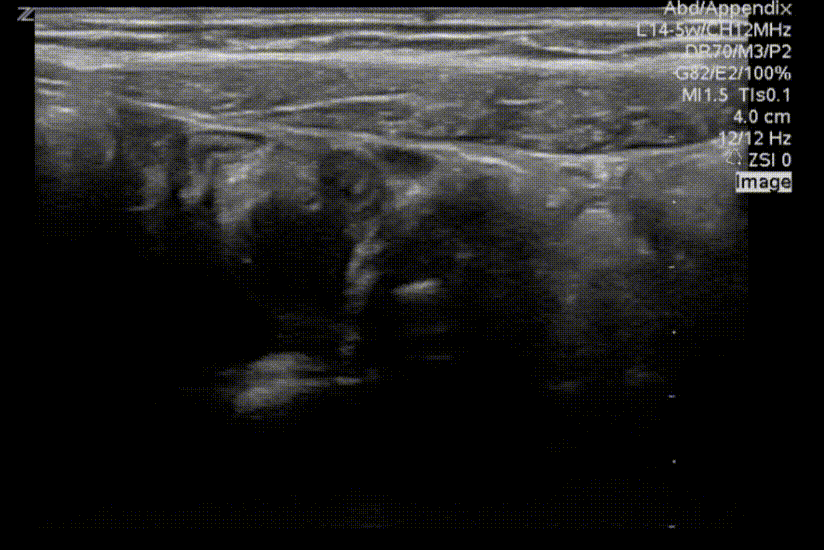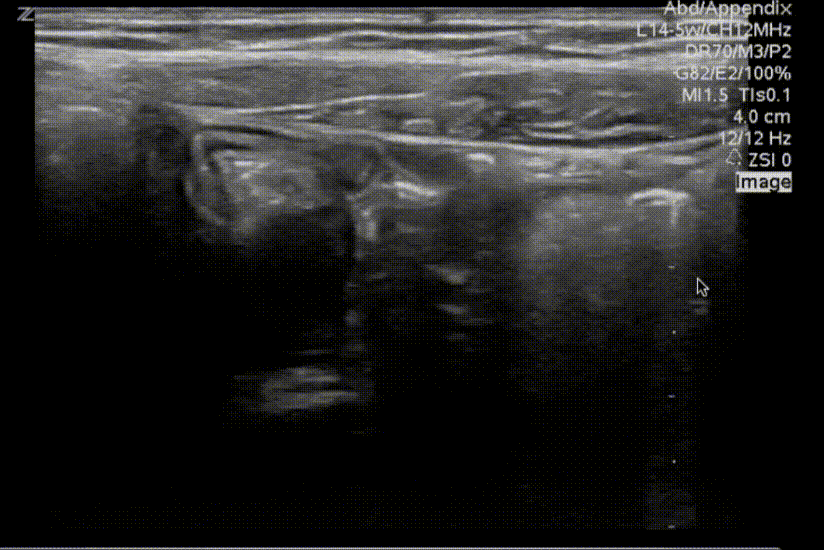
A transverse clip of the right lower quadrant is shown below:
What structure is highlighted in the clip?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 27
16. Question
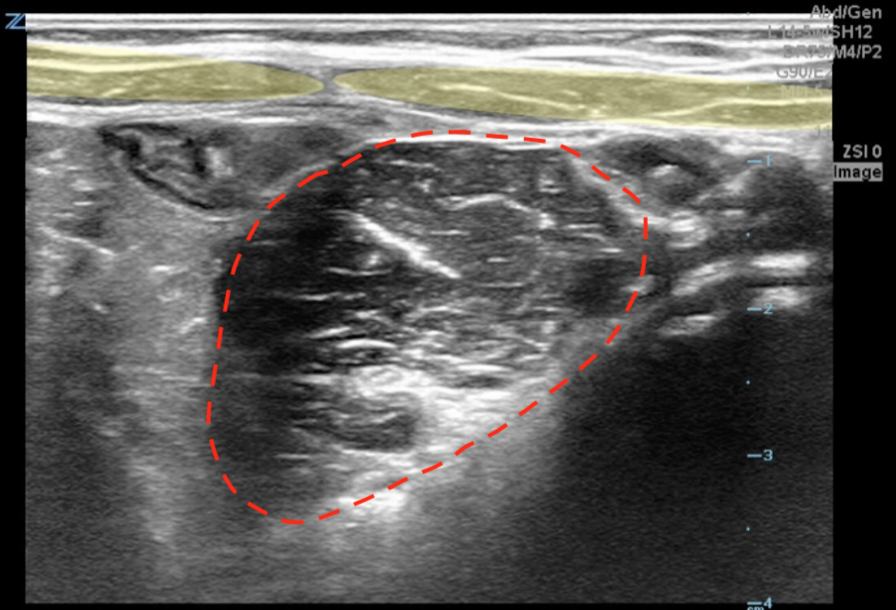
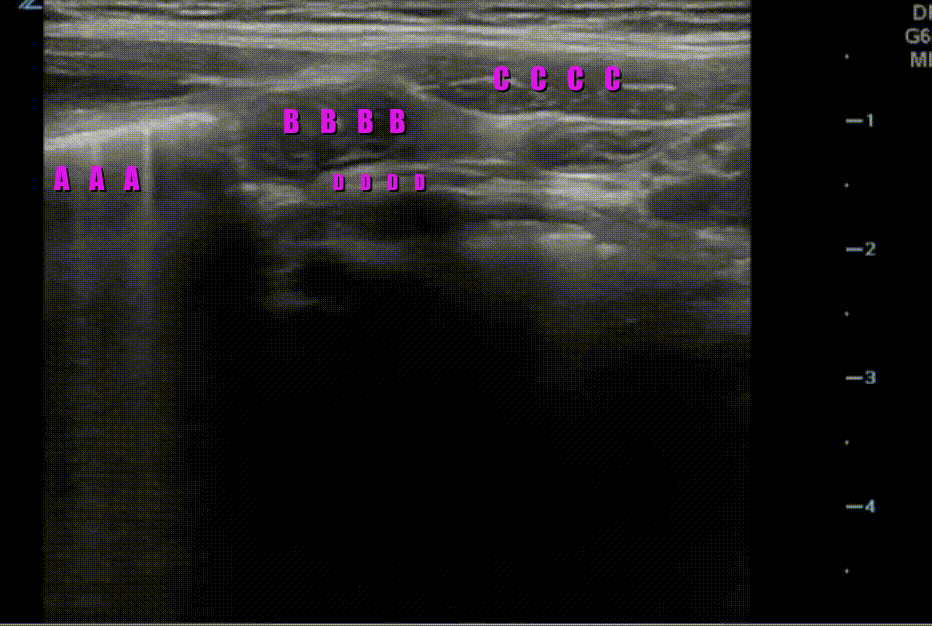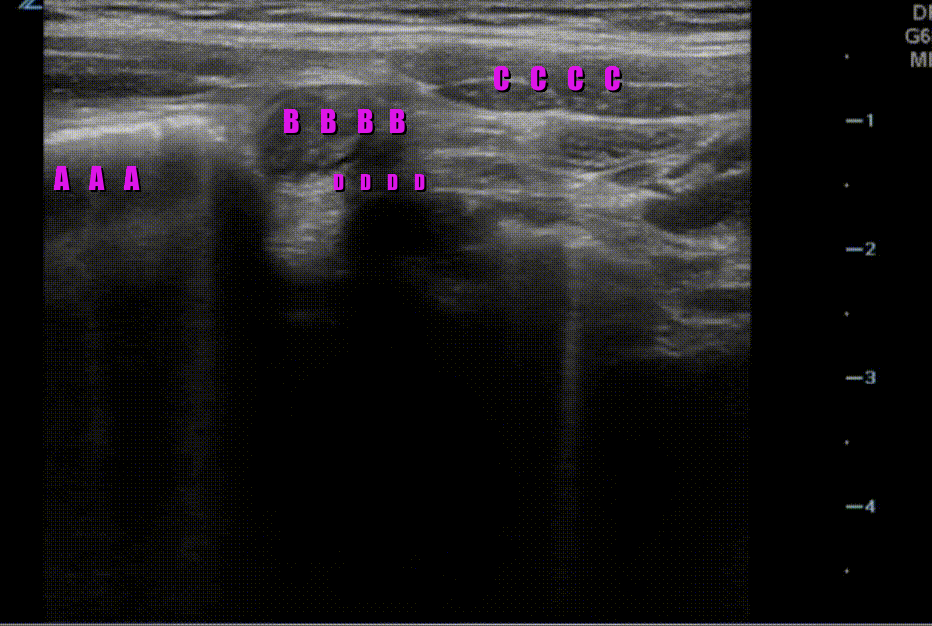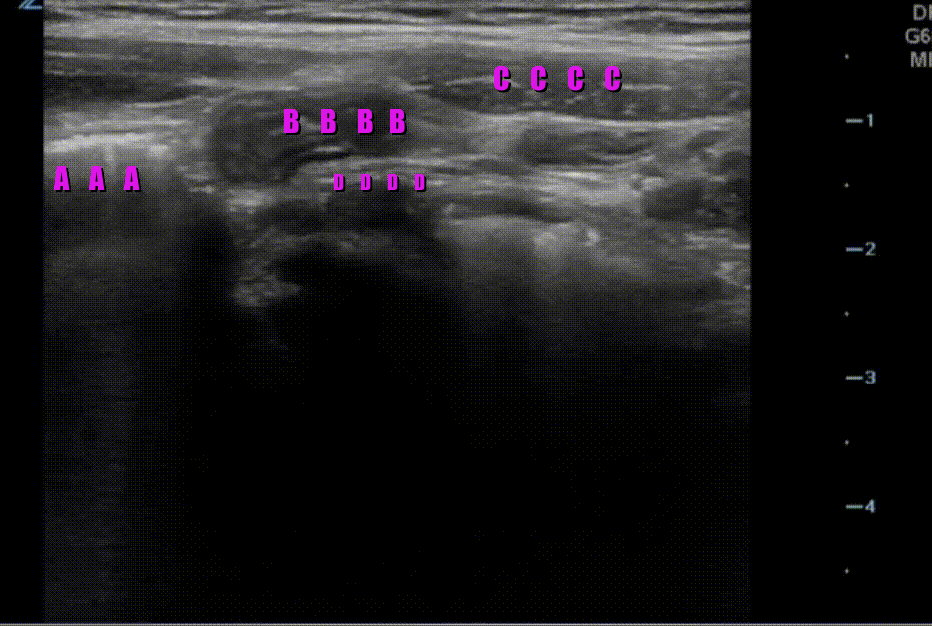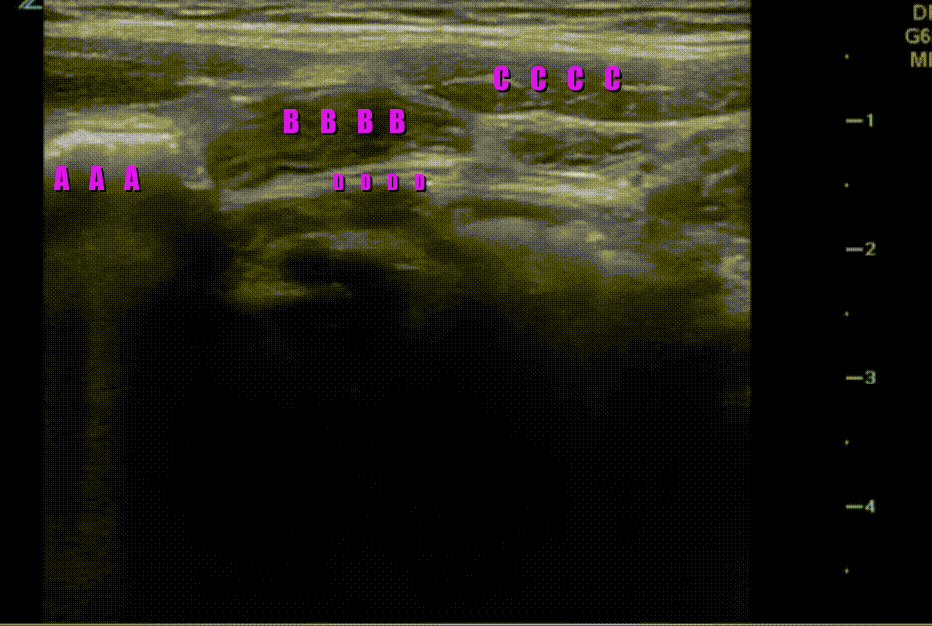
A transverse clip of the right lower quadrant is shown below:
A is the large intestine. Identify the structure labeled “B”
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 27
17. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 27
18. Question
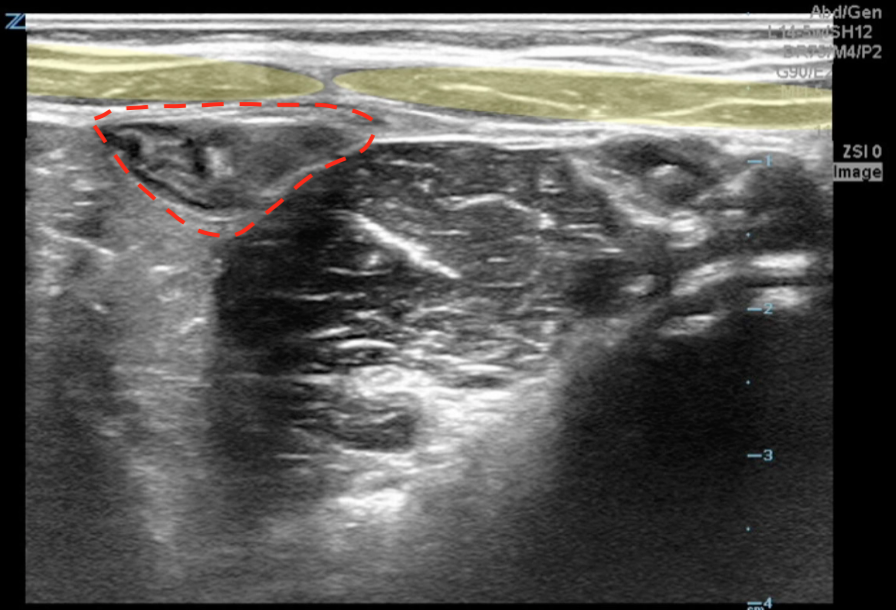
A transverse view of the right lower quadrant is shown below. What is the peristalsing structure shown in the clip?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 27
19. Question
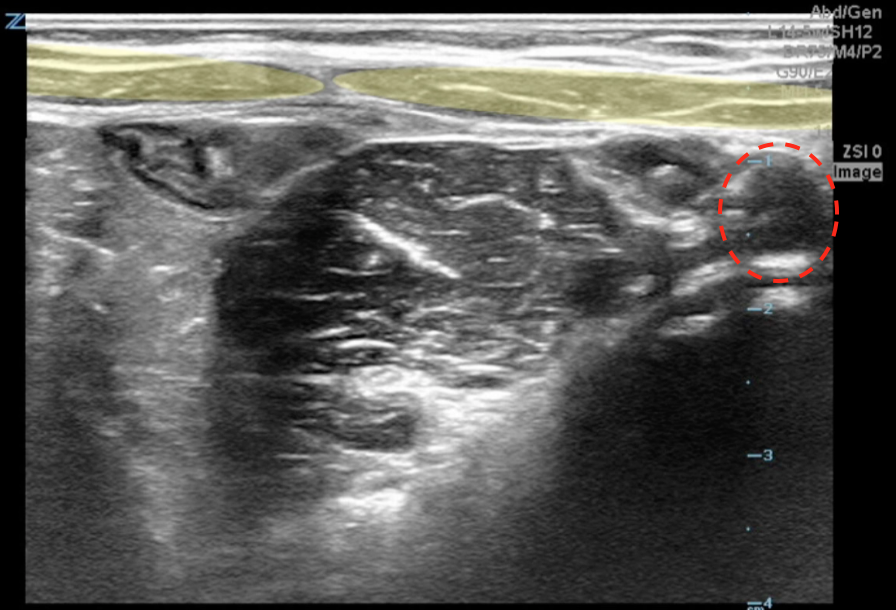
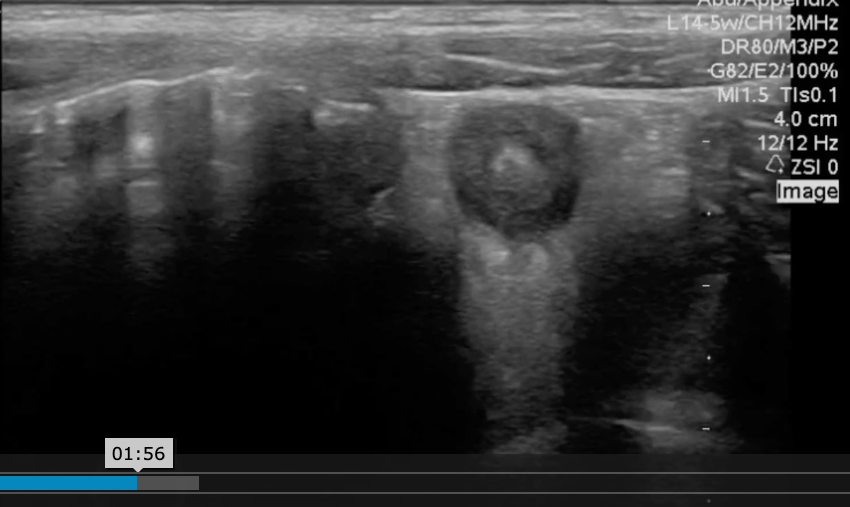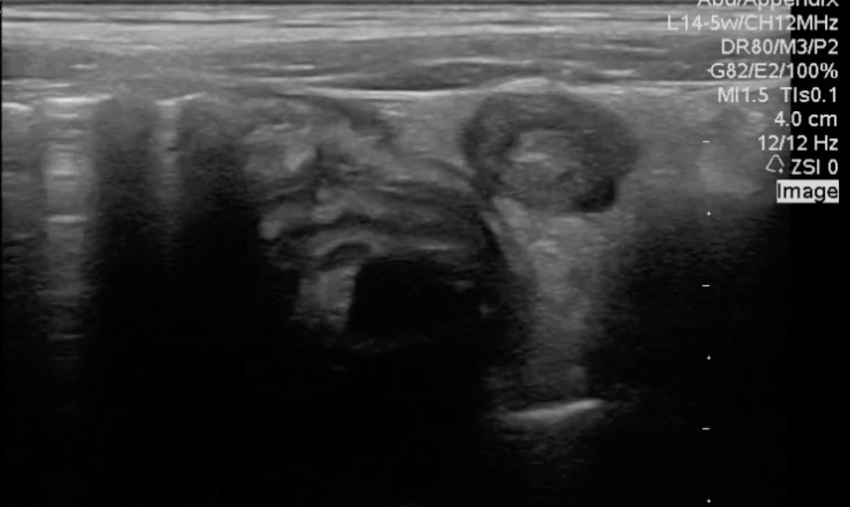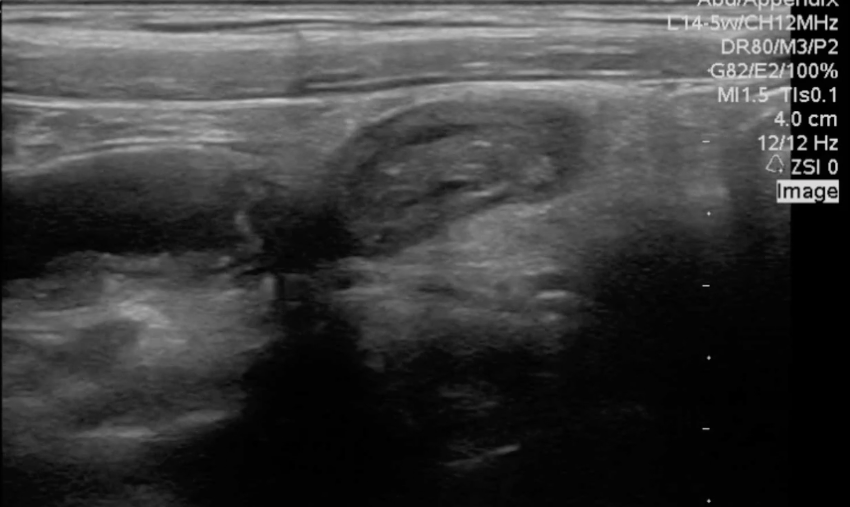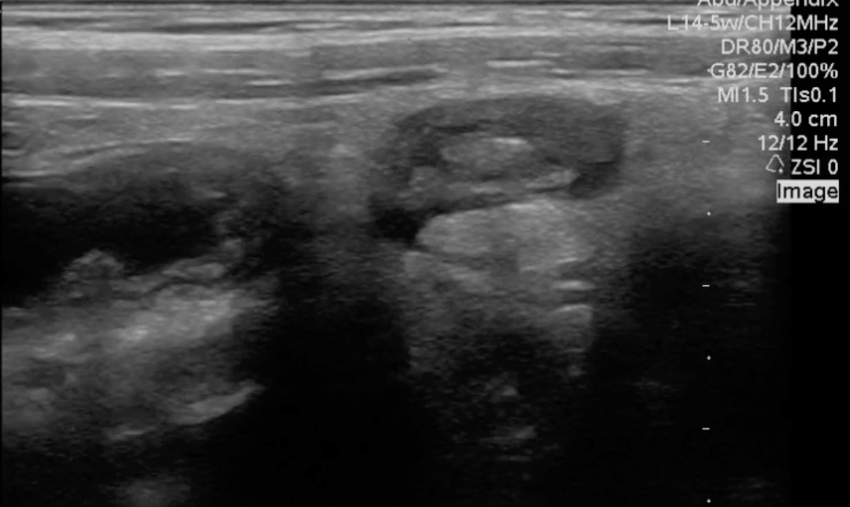
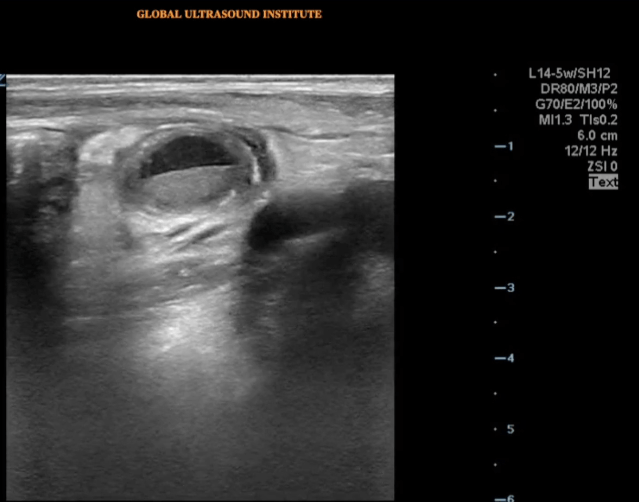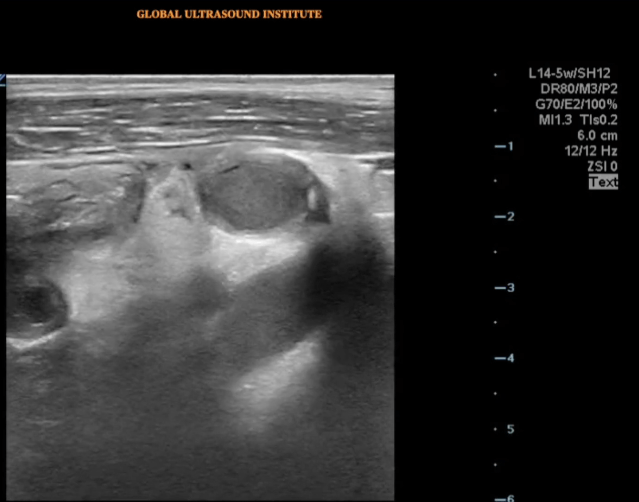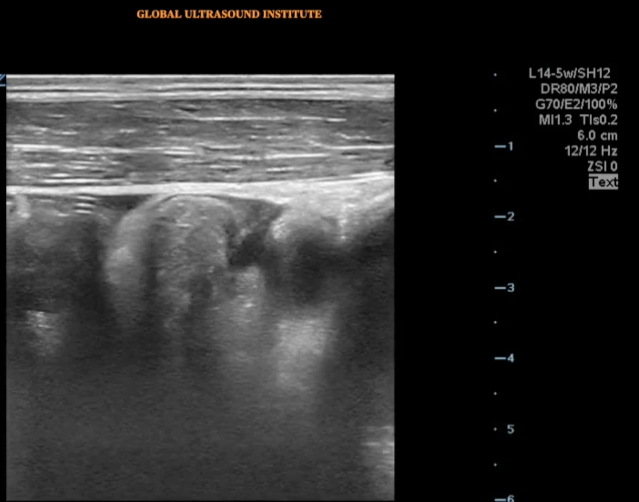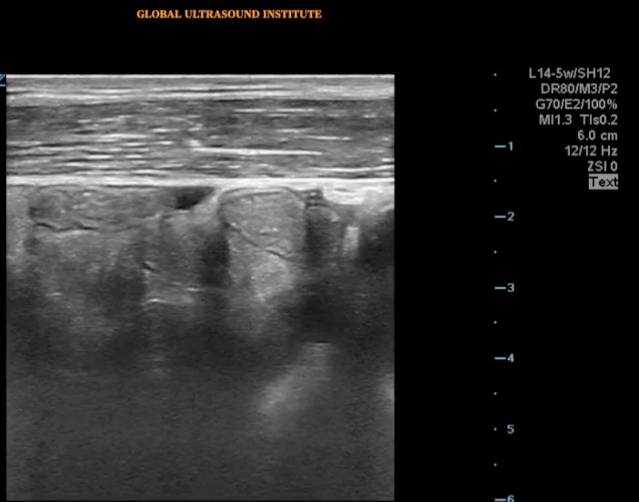
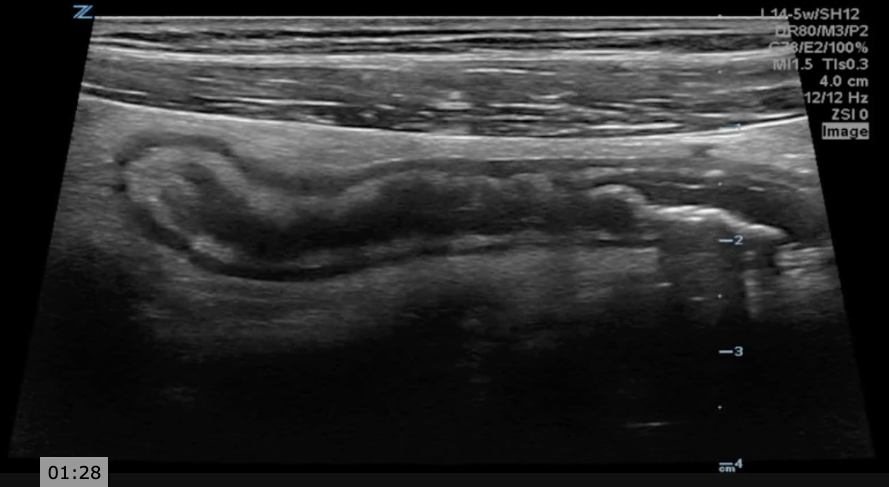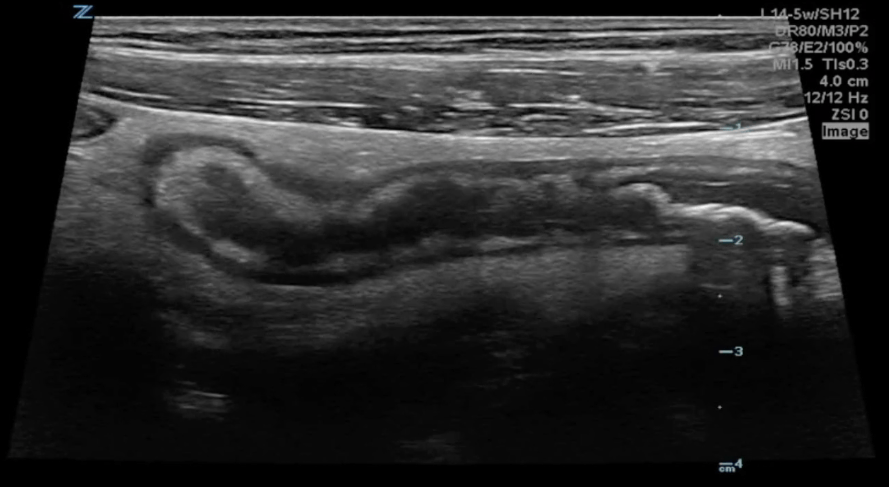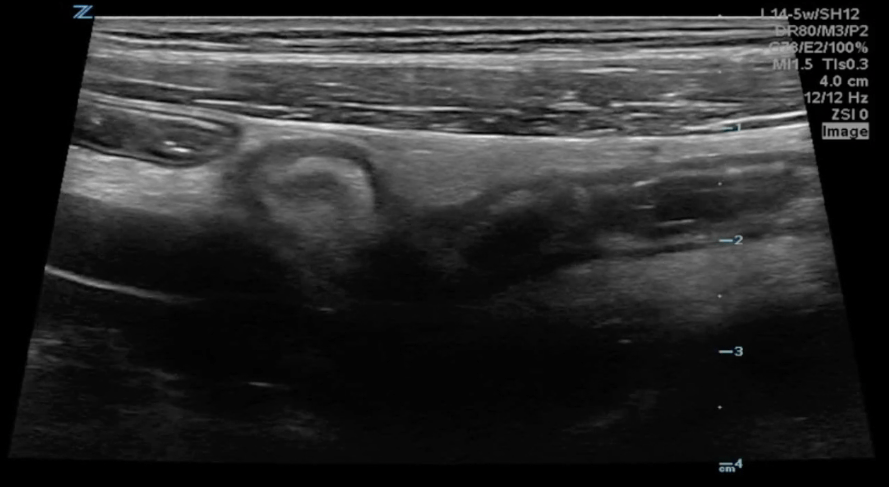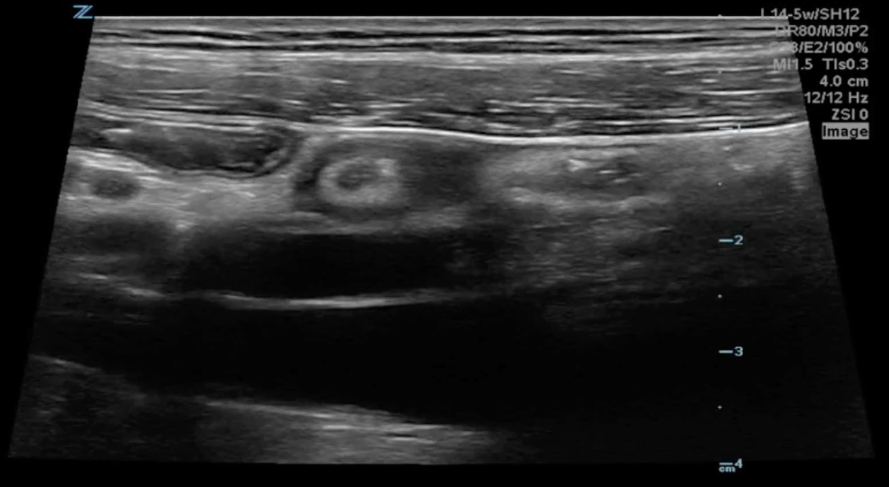
A longitudinal view of the right lower quadrant is shown below. Which of the labeled structures is the appendix?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 27
20. Question
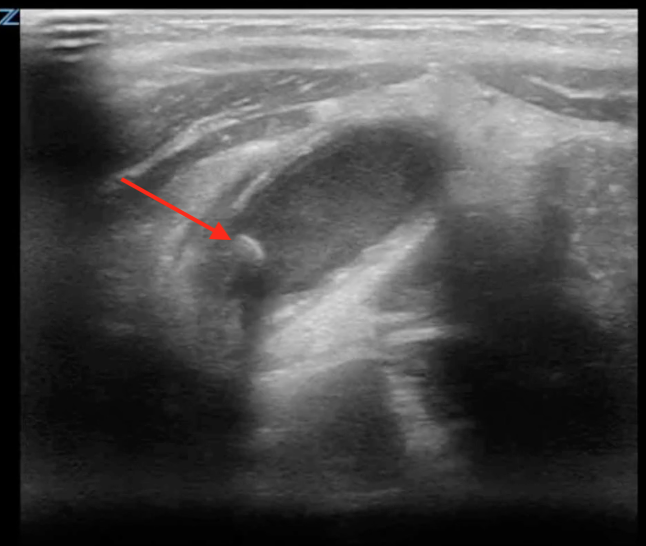
A transverse image of the right lower quadrant is shown in the image. What is the arrow pointing to?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 27
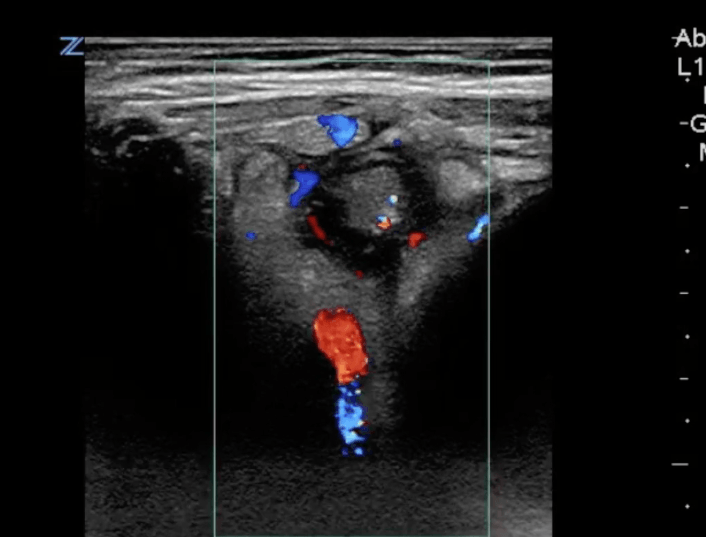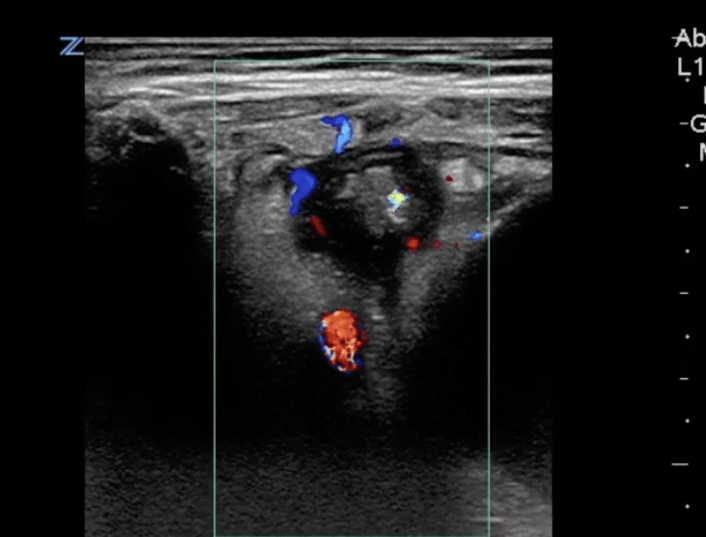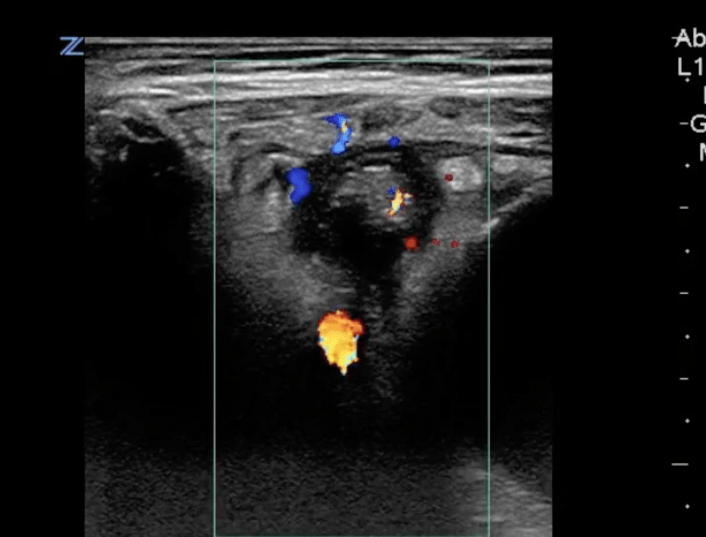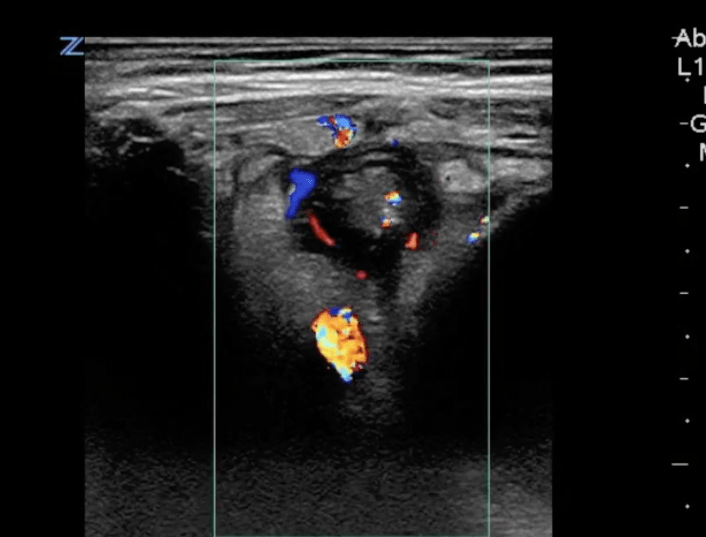
21. Question
A transverse image of the right lower quadrant is shown. What diagnosis is associated with the finding in the clip:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 27
22. Question
An 8 year old child presents with <24 hours of fever, nonbilious/nonbloody vomiting, and constant right lower quadrant pain.. A transverse view of the right lower quadrant is shown:
Which of the following diagnoses is the most likely cause of this child’s symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 27
23. Question
An 8 year old child presents with <24 hours of fever, nonbilious/nonbloody vomiting, and constant right lower quadrant pain. A longitudinal view of the right lower quadrant is shown:
Which of the following diagnoses is the most likely cause of this child’s symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 27
24. Question
An 8 year old child presents with <24 hours of fever, nonbilious/nonbloody vomiting, and constant right lower quadrant pain. A longitudinal view of the right lower quadrant is shown:
Which of the following diagnoses is the most likely cause of this child’s symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 27
25. Question
An 8 year old child presents with <24 hours of fever, nonbilious/nonbloody vomiting, and constant right lower quadrant pain. A transverse view of the right lower quadrant is shown:
Which of the following diagnoses is the most likely cause of this child’s symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 27
26. Question
A 7 year old non-verbal boy with a history of multiple admissions for inpatient “clean outs” for constipation presents to the emergency department with 2 days of vomiting and poor appetite. He is unable to localize his pain, but parents indicate that he has not eaten all day and is crying and yelling since last night. Exam is significant for an uncomfortable, febrile child who does not relax his abdomen with palpation. You administer analgesia for pain and perform POCUS or appendicitis.
Which of the following diagnoses is suggested by the sonographic findings above?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 27
27. Question
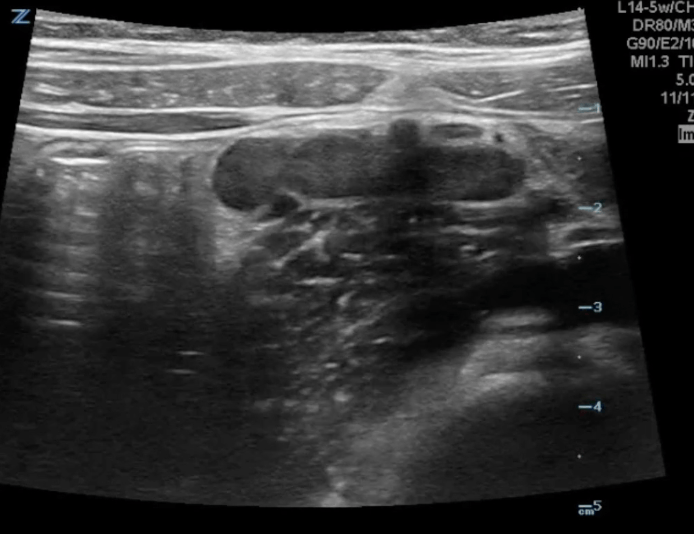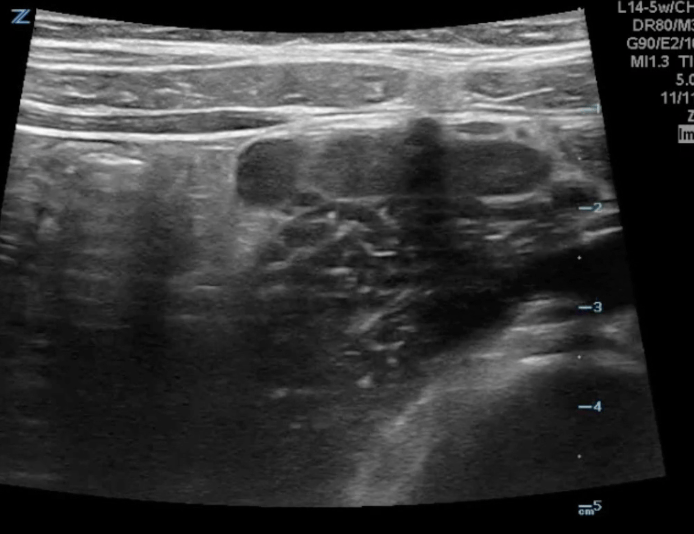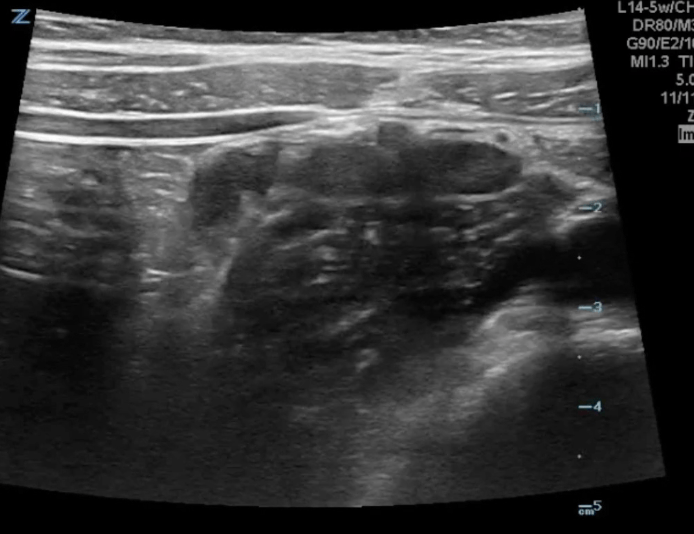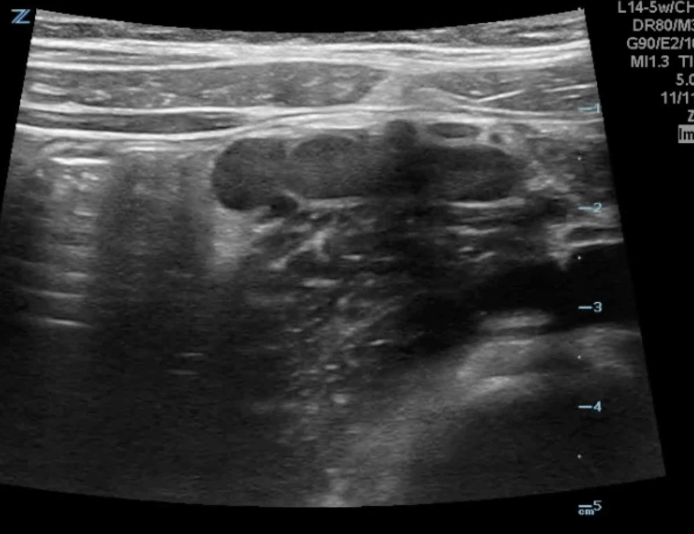
A 5 year old uncircumcised boy with no medical problems presents to the emergency department with 3 days of vomiting, fever, poor appetite, and abdominal pain. He has not had diarrhea, has not eaten today, and refused to walk into the emergency department. On exam, he is very fearful and cries producing lots of tears the moment the examiner enters the room and pushes the examiner away when the abdominal exam is attempted. Aside from fever of 38.5 C and tachycardia (attributed to crying and fever), his vital signs are normal. You perform a point of care ultrasound with the aid of child life but due to bowel gas you are unable to locate the appendix. You do find the following in multiple locations in the abdomen:
Blood work returns with a WBC of 15 with a neutrophilic predominance. Which of the following is your next step in assessment?
CorrectIncorrect
Contact form website
Contact form website
"*" indicates required fields
CONTACT US
Get in touch with our team to know more about GUSI.
PRE-REGISTRATION | POCUS FOR PRIMARY CARE IN PERSON COURSE OCT. 2025
Tentative Dates: October 17-18, 2025 | San Francisco, CA
PRE-REGISTRATION | POCUS FOR PRIMARY CARE IN PERSON COURSE APRIL 2025
Tentative Dates: April 2025 | San Francisco, CA
PRE-REGISTRATION | GUSI-OHSU Musculoskeletal Ultrasound for Primary Care & Joint Injection Cadaver Course
Tentative Dates: June 7-8, 2025, Portland, OR
PRE-REGISTRATION | OB POCUS ESSENTIALS COURSE JAN 30 - FEB 2
Jan 30th to Feb 2nd 2025
[elementor-template id=”3620″]