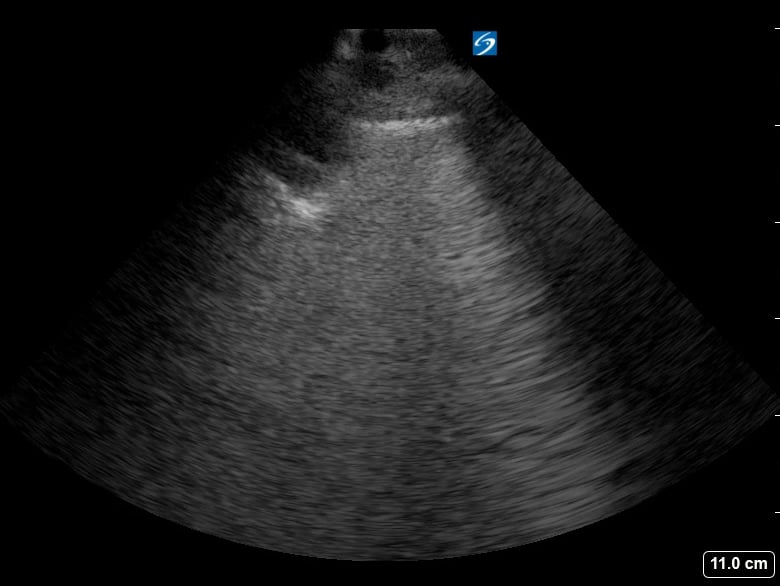
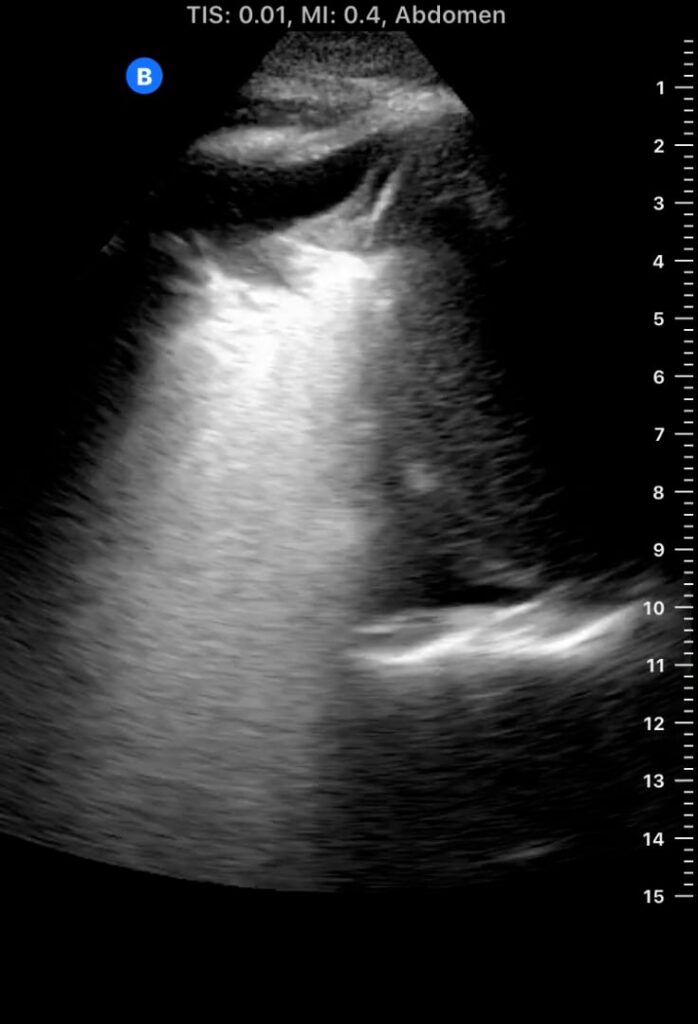
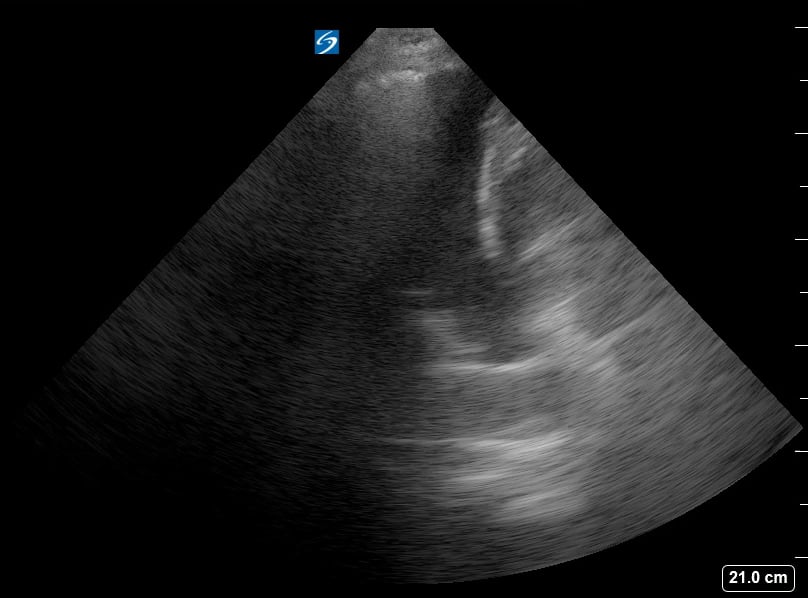
Lung consolidation in medical ultrasound refers to the solidification of lung tissue due to the accumulation of fluid, cells, or other substances, replacing the air within the alveoli. This pathological change commonly indicates conditions like pneumonia or atelectasis. On ultrasound, consolidated lung appears hyperechoic (bright) with a tissue-like echotexture, often resembling the liver (hepatization).
Identifying lung consolidation via ultrasound is crucial for rapid diagnosis and management in acute care settings. This non-invasive imaging technique allows clinicians to visualize air bronchograms (air-filled bronchi within consolidated tissue) and pleural effusions, aiding in differentiation from other lung pathologies. Ultrasound offers a portable and radiation-free alternative for bedside assessment of lung parenchyma, optimizing patient care.