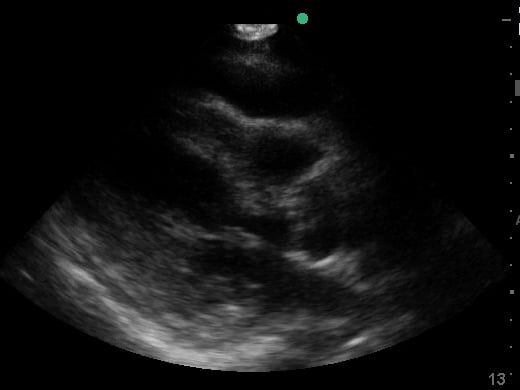
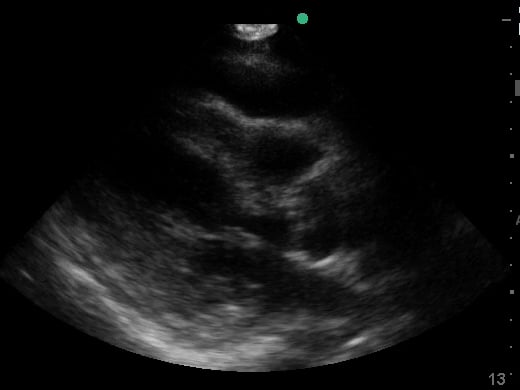
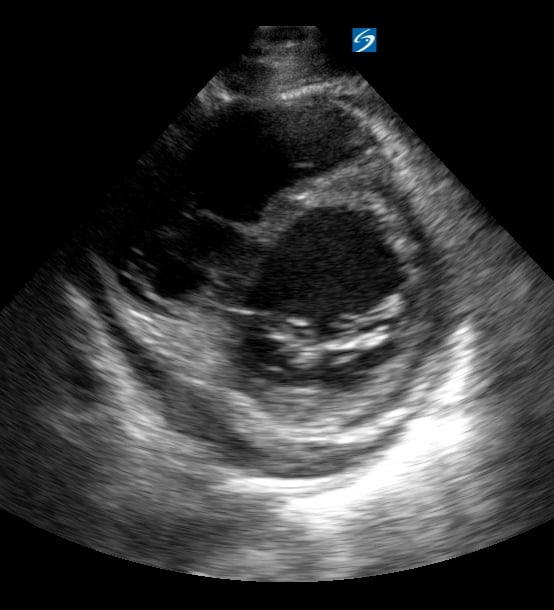
Pericardial effusion in cardiac ultrasound refers to an abnormal accumulation of fluid within the pericardial sac, the double-layered membrane surrounding the heart. This condition can impede the heart’s ability to fill and pump blood effectively, potentially leading to cardiac tamponade, a life-threatening emergency. Early detection through echocardiography is crucial for timely medical intervention and improved patient outcomes.
Utilizing medical ultrasound, healthcare professionals can accurately identify and quantify pericardial effusions, assessing their size, location, and hemodynamic impact. Ultrasound imaging provides real-time visualization of the fluid build-up, enabling precise diagnosis and guiding potential therapeutic procedures such as pericardiocentesis. This non-invasive technique is indispensable for managing cardiac health and preventing severe complications.