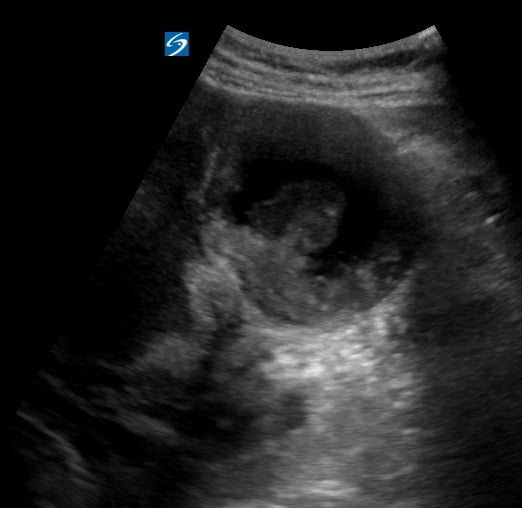
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas or myomas, are common benign (non-cancerous) growths of the uterus. They originate from the smooth muscle cells of the uterine wall and can vary widely in size, number, and location. In OBGYN, fibroids are a frequent finding during gynecological exams and can cause a range of symptoms, including heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, pressure on the bladder or rectum, and infertility.
Ultrasound is the primary imaging modality for diagnosing and characterizing uterine fibroids due to its non-invasiveness and real-time capabilities. Sonography allows for the visualization of fibroid size, location (e.g., submucosal, intramural, subserosal), and internal features, aiding in treatment planning. Understanding fibroid characteristics via ultrasound is crucial for effective patient management in women’s health.